Components of DBMS
Learn via video course

Overview
The term Database Management System (DBMS) refers to a group of computer programs contained in a software package that has been specially created for the development, maintenance, and use of databases while following the necessary security measures. There are various components of DBMS which help in increasing the usefulness of the database and its environment. We will be discussing each component in this article.
Scope
In this article we will learn about:
- Data and Database management system.
- The various components of DBMS that are used to increase the usefulness of the database and its environment.
- Uses of a Database management system.
This article does not cover query implementation, or the working of DBMS, and focuses on a generalized DBMS software irrespective of any type of DBMS.
Introduction
All of the individual objects that are kept in the database are referred to as data. It must be handled and kept secure in a way so that only authorized users can access it, make modifications, or store it quickly. We should first understand what a DBMS is before learning about its components.
Data: Data refers to the raw facts or numbers. The term "raw" denotes that they have not undergone any processing, hence they have no specific significance. Example – 42, ABC, etc.
Database: Database is a collection of interrelated data. It is saved in various forms such as tables, documents, and trees. Example - (Table)
| EmpID | Employee Name | Age |
|---|---|---|
| 110 | Albert | 25 |
| 120 | Kevin | 30 |
| 121 | George | 28 |
Management System: It is a piece of software that facilitates effective database data retrieval, insertion, and deletion and organizes the data into things like tables, views, schemas, reports, etc.
DBMS: Database Management System = Data + Management System.
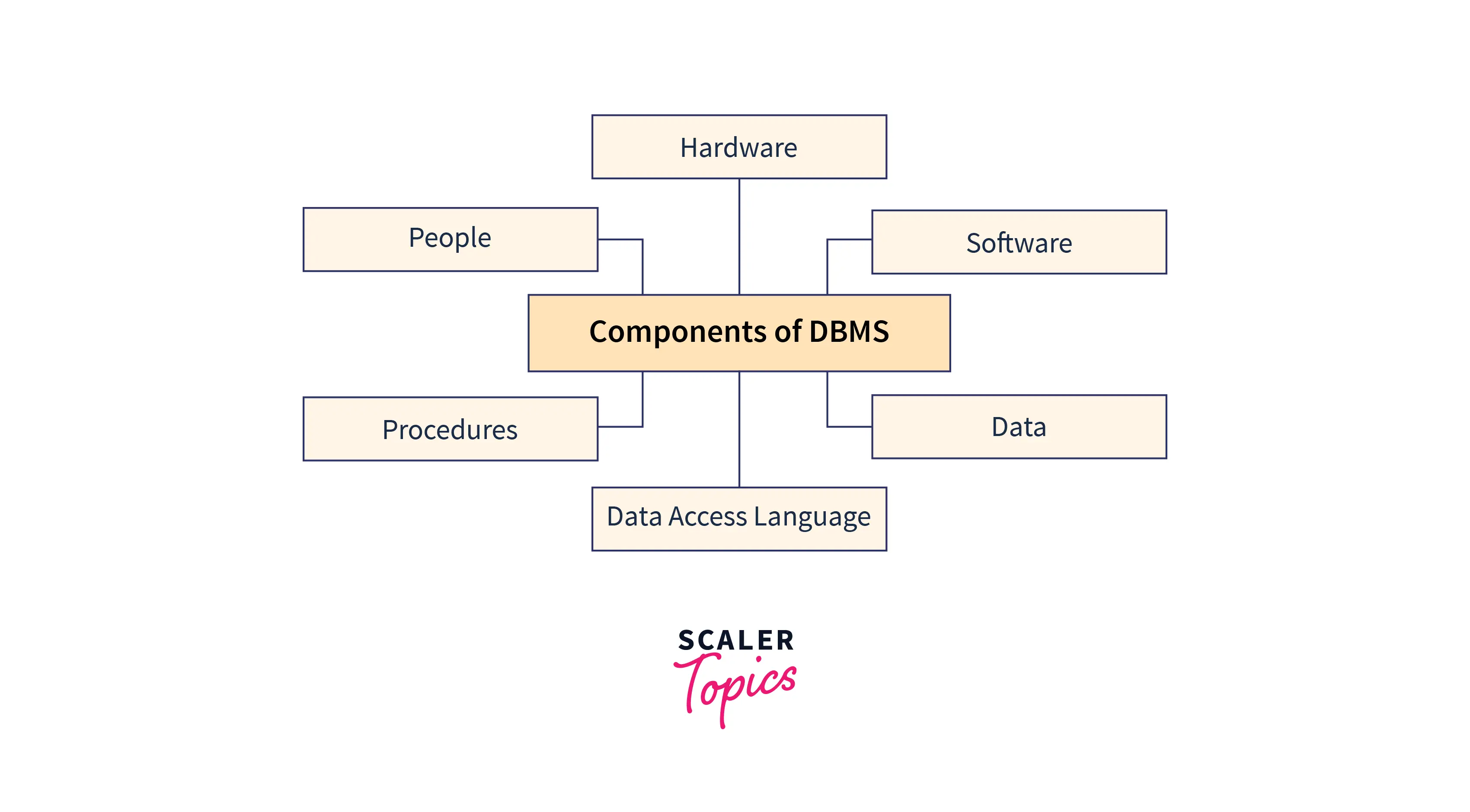
Components of DBMS
The Database Management System contains several components and each component has a specific function in the DBMS environment. The main components of DBMS are:
- Hardware
- Software
- Data
- Procedures
- Database Access Language
- People
Hardware
- The term "hardware" describes a group of physical electronic components, such as computers and associated I/O (input/output) devices, storage devices, and other structural elements.
- To help users in creating, accessing, or maintaining databases, hardware interacts with software to build an interface between a computer and a physical system.
- Hardware is a necessity for DBMS implementation and use. The mouse, keyboard, RAM, ROM, and hard drive all act as DBMS hardware when we run any database management system, such as Oracle, MySQL, etc., on our PC.
- When we use Oracle or MySQL on a PC, the hard drive, keyboard of the computer as well as its RAM and ROM all become a part of the DBMS hardware.
Software
- The software comprises the majority of a database management system.
- Software is a set of programs that provide instructions to a machine. The complete collection of scripts, instructions, and processes used to run a computer system is referred to as software.
- Software tells a computer's hardware how to carry out a task.
- Between the physical database and the users, the database management system(DBMS) serves as the software. The DBMS handles every request a user makes to access the database.
Data
- Data refers to the raw facts or numbers. The term "raw" denotes that they have not undergone any processing, hence they have no specific significance. Example – 42, ABC, etc.
- All of the individual objects that are kept in the database are referred to as data.
- The introduction of a database management system was driven primarily by the need to store data. In a regular database, both data and metadata(information about actual data) are kept.
Procedures
- Procedures are broad instructions for utilizing a database management system.
- This comprises steps for installing a DBMS, logging in and out of DBMS software, managing databases, creating backups, and reports, changing and modifying the database structure, etc.
- Access control, data validation, and reducing network traffic between clients and DBMS servers are all possible with procedures.
Database Access Language
- Database Access Language is a simple programming language created for writing commands to access, insert, update, and delete data contained in any database.
- A user may create commands in the Database Access Language and submit them to the database management system (DBMS) for processing. DBMS will translate and carry out the commands.
- Using the access language, a user can build new databases, and tables, enter data, retrieve stored data, update data, and remove data.
- A database language is comprised of two languages:
- Data Definition Language (DDL): At the physical, logical, and external levels, DDL implements database schema (structures the database). Example:
- DESCRIBE
- ALTER
- COMMENT
- SHOW
- USE
- CREATE
- DROP
- Data Manipulation Language (DML): It is used to access a database. To obtain, change, insert, and delete data from the database, DML statements are used. Example:
- INSERT
- LOCK
- CALL
- EXPLAIN PLAN
- UPDATE
- DELETE
- Data Definition Language (DDL): At the physical, logical, and external levels, DDL implements database schema (structures the database). Example:
People
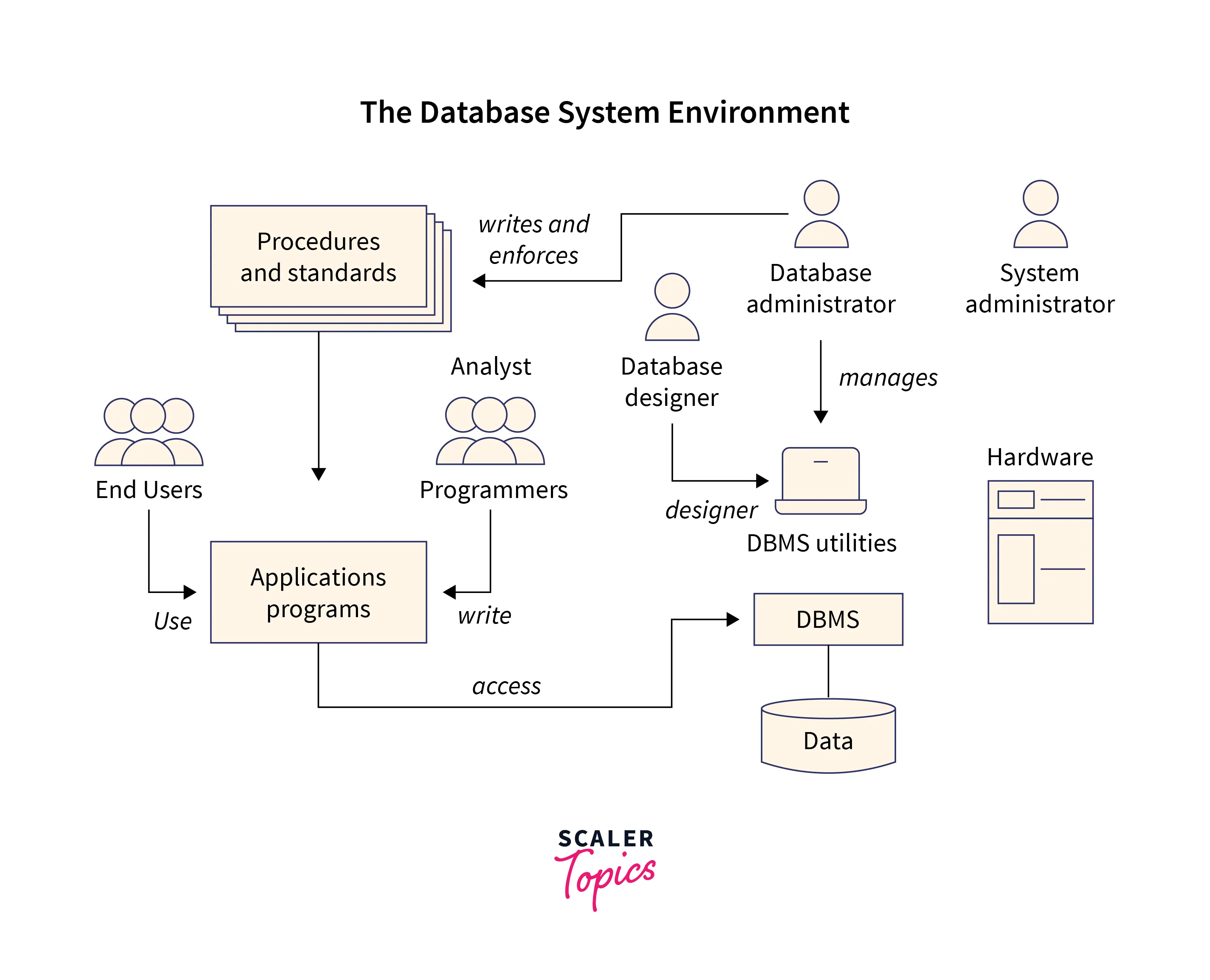
- Various types of people control and administer the databases and carry out various operations on the databases in the DBMS. These include Software engineers, End-user, Database Administrators, etc.
- Software Engineers: Massive amounts of data may be handled by them, and they are also capable of creating and changing databases, as well as identifying and fixing database problems.
- The person who supervises the entire database management system is the database administrator. The DBMS's security, availability, license key management, user account, access management, etc. are all handled by the DBA.
- Therefore, people are considered a vital component of DBMS.
Other DBMS Components
-
Query Processor: It is a parser, optimizer, and query execution engine for Structured Query Language (SQL). To deliver the desired outcomes, the Query Processor interacts with the Database Server and executes SQL queries following a defined plan. The most efficient execution strategy is picked by the optimizer. In the stage of optimization, the Query Processor chooses-
- The sequence in which joins are carried out.
- Applying constraints in a particular sequence.
- The method which gives the best performance.
-
Run Time Database Manager: A runtime database manager verifies user authorizations, executes authorized queries, and chooses the approach that yields the best query results. It also assures data integrity and manages any task that requires managing queries and runtime data.
-
Data Manager: It is also known as the cache manager, is in charge of managing the data in the database and giving the system a recovery that enables it to restore the data in the event of a failure.
-
Database Engine: To meet the demands of the most demanding data-consuming applications, this service acts as the core component for storing, processing, and securing data. It offers regulated access and quick transaction processing. To process data for online transaction processing or online analytical processing, relational databases are frequently created by the database engine.
-
Data Dictionary: This is a separate area in a database where details about the database itself are kept. An organization uses a data dictionary, which is a collection of read-only tables and views, to verify that the data represented in databases is in accordance with the dictionary's standards. Read more about Data Dictionary in DBMS.
-
Report Writer: It is software that extracts data from one or more files and presents the data in a predefined format. The majority of report writers enable the user to pick records that satisfy particular criteria, show chosen fields in rows and columns, and format the data into various charts.
Uses of DBMS
- They keep data and offer tools for searching for certain entries within a set of data.
- To manage the data, they keep special information about the data known as metadata in DBMS and this metadata is not shown to the user looking at the data.
- They can deal with situations when multiple users wish to access (and sometimes modify) the same data entries. Data should therefore be redundant.
- They monitor security constraints as well as access permissions (who may view the data and make changes to it).
- The database needs to respond to queries quickly when there are plenty of people asking them. As a result, the data response is quick.
Conclusion
- DBMS refers to a group of computer programs contained in a software package that has been specially created for the development, maintenance, and use of databases while following to the necessary security measures. DBMS comprises 6 main components namely:
- Hardware
- Software
- Data
- Procedures
- Database Access Language
- People
- Hardware describes all physical electronic components, such as computers and associated I/O (input/output) devices, storage devices, and other structural elements whereas, Software comprises the majority of a database management system that manages all the data.
- Data refers to the raw facts or numbers. To help write commands to access, insert, update, or delete data contained in any database Database Access language is used.
- Procedures comprise steps for installing a DBMS, logging in and out of DBMS software, managing databases, creating backups, and reports, changing and modifying the database structure, etc.
- People comprises various groups like Software engineers, Database administrator, end users, etc, who access, store, and perform operations on the database.
- We also learned about other components of DBMS like query processor, data manager, report writer, etc to make a DBMS fully functional and optimized.
- DBMS also helps in storing data, and metadata; implementing security constraints, and query optimization in DBMS for faster response to the client.
