Queue in C++
Learn via video course

Overview
Suppose you want to order food in a fast-food chain restaurant. You see a queue of people, and you join the queue where the last person of the queue is standing. A person standing before you in the queue will also reach the counter before you. So you can place your order only when you reach the front of the queue.
Queues in C++ work similarly.
A queue is a linear data structure that follows FIFO(First in First Out) technique. This means the element pushed first into the queue will also be the first element to come out of it.
Scope
- This article discusses about queue data structure in C++ with examples.
- It describes various functions in a queue.
- It briefly covers priority queue(a variation of queue) in C++.
- It explains the difference between a stack and a queue.
- It discusses various applications of queues.
Introduction
A queue is a linear data structure in which insertion takes place at the back, and deletion takes place from the front. It works on the principle of First In First Out(FIFO).
There are many variations of queue present in C++, such as deque, priority queue, double-ended priority queue. It has many interesting applications in operating systems, networking, etc.
Syntax
The syntax of declaring a queue in C++ is:
The header file required to use queue in C++ is:
Basic Operations
There are two basic operations in queue: enqueue and dequeue.
- Enqueue: When we add an element to a queue, it is said to be an enqueue operation. If the queue is full, we cannot add more elements to it. Such a condition is called an overflow condition. We use the push function to perform an enqueue operation in a queue. Time Complexity - O(1)
Syntax
- Dequeue: When we remove an element from a queue, it is said to be a dequeue operation. If the queue is already empty, i.e., there are no elements in the queue, we cannot remove elements from it. Such a condition is called an underflow condition. We use the pop function to perform a dequeue operation in the queue. Time Complexity - O(1)
Syntax
Note: Since a queue works on the FIFO technique, the element which was pushed in first will pop out first as well, i.e., the relative order of elements in a dequeue operation is the same as the enqueue operation
Diagrammatic Illustration
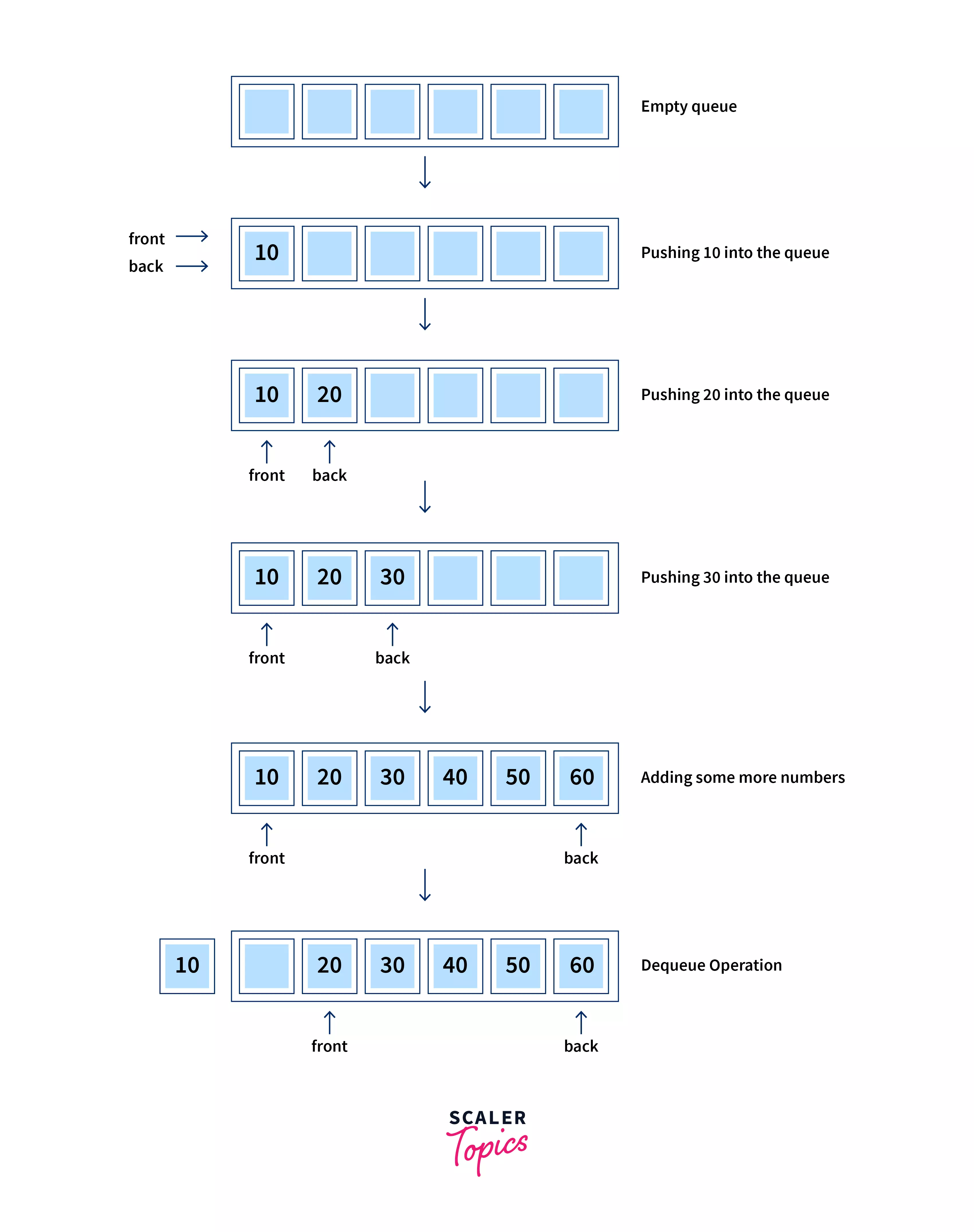
Code Example
Below is an example showing the simple working of queue in c++.
Output
Explanation We declare a variable q of the type queue and perform enqueue and dequeue operations using the push() and pop() functions, respectively. The front() function returns the first element in the queue. The empty() function checks whether the queue has any element in it.
Functions Described in a Queue
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| empty() | This function returns 0 if the queue is not empty and a non-zero value if the queue is empty. |
| front() | This function returns the value of the first element in the queue. The first element is the one that was pushed into the queue before all the elements were present in the queue. |
| back() | This function returns the value of the last element in the queue. The last element is the one that was pushed into the queue after all the elements present in the queue. |
| push(a) | This function inserts an element to the end of the queue. |
| pop() | This function removes the first element from the queue, i.e., the element returned by the front method. |
| size() | This function returns the size of the queue. |
| swap() | This function exchanges the contents of the two queues. The two queue types should be of the same type. |
| emplace() | This function constructs and inserts a new element at the end of the queue. |
Note: The push() creates a copy of the element and appends it to the end of the queue while emplace() creates the new instance in-place at the end of the queue. The end result of both the functions is completely same.
Example Showing Basic STL Queue Functions
The queue in c++ is predefined in the Standard Template Library, here is an example to describe the basic working and associated methods of STL Queue;
Output
Explanation
We declare a queue q of type int. We perform an enqueue operation by pushing elements inside the queue. We then print the first element, last element, and the size of the queue. We then create another queue q2, and perform several operations on it. Then we exchange the contents of the two queues using the swap function. Then we perform dequeue operation on the queue q by using the pop function until the queue is empty.
Introduction to Priority Queue
Priority queues are a special types of queues in which the elements are ordered on the basis of their priority. They are of two types.
-
Max-priority queue: The first element in the queue is the greatest of all elements. All the elements are in non-increasing order. It is implemented using max-heap. By default, C++ creates a max-priority queue.
-
Min-priority queue: The first element in the queue is the smallest of all elements. All the elements are in non-decreasing order. It is implemented using a min-heap.
All the methods such as push(), pop(), empty(), size(), swap(), emplace() described above can be applied on priority queues as well.
Note: Queue has a front() method that returns the first element of the queue. We have the top method for the priority queue for the same.
Syntax of Priority Queue
The syntax of priority queue(max-heap) is:
The syntax of priority queue(min-heap) is:
Note: It is present in the queue header file in the C++ Standard Template Library.
Stack vs Queue
| Stack | Queue |
|---|---|
| A stack is a linear data structure in which the elements are inserted and deleted from the end of the stack. | A queue is a linear data structure in which the elements are inserted from the last and deleted from the front of the queue. |
| It is based on the LIFO(Last In First Out) technique. | It is based on the FIFO(First In First Out) technique. |
| It is used in expression matching and evaluation, string parsing, backtracking, memory management, recursive problems, etc. | It is used in mailing lists, CPU scheduling, Disk scheduling, routers, switches, semaphores, etc. |
Application of Queue
Queue in c++ have several real life usecases, few of them are listed below.
- It is used as a waiting list when a resource is shared among multiple processes, e.g., CPU scheduling, disk scheduling.
- It is used to handle interrupts in operating systems.
- It is used in semaphores, spooling in printers, FIFO scheduling.
- It is used in networking systems where data is transferred asynchronously, e.g., IO buffers, files IO, etc.
- It is used in routers and switches as well as in mailing lists.
- It is used for maintaining playlists in music applications.
Conclusion
- A queue in c++ is a linear data structure that is based on the FIFO(First In First Out) principle.
- A enqueue operation(insertion) is performed at the end of the queue.
- A dequeue operation(deletion) is performed from the front of the queue.
- All the three operations, insertion, deletion, and access have O(1) time complexity.
- Priority queues are a special types of queues in which the elements are ordered on the basis of their priority.
- A stack is a linear data structure that is based on the LIFO(Last In First Out) principle.
- Queues are used for CPU scheduling, handling interrupts, semaphores, networking systems, etc.
