What Are Data Structures and Algorithms?
Learn via video course

Overview
More precisely, a data structure is a collection of data values, the relationships among them, and the functions or operations that can be applied to the data
Scope of Article
- This article tells about data structures.
- Definition of important terms.
- This article tells about characterstics of algorithm.
- This article tells about data flow of algorithm.
- How to write algorithms.
- Factors of an algorithm.
Takeaways
A data structure is a named location that can be used to store and organize data. And, an algorithm is a collection of steps to solve a particular problem.
The word “algorithm” right away would make you think of technical stuff and make it seem daunting. So today, we are going to try to understand it the easy way.
Spoiler alert: It is not as daunting as it sounds.
Let us suppose it’s your mom’s birthday but no bakeries are open due to Covid related restrictions. So you decide to bake a cake for her. But you do not know how to do it. The next thing you do is head over to everyone’s know-it-all best friend- Google. You look up a recipe that you like and make a note of it. The recipe describes step-by-step what you need to do to bake the perfect cake.
Now armed with the recipe, you gather the ingredients, mix them up as per the steps and bake it in the oven. And voila, after a while, the cake is ready and you’re successful at your task.

It sounds pretty simple, right?
Well, let me tell you what all you learned from this hypothetical scenario-
- You learnt what an algorithm is
- You learnt about the characteristics of an algorithm
- You also learnt how data flows in an algorithm
Right now, you must be wondering how you learnt all these things from just baking a cake. So let’s wait no more and deep dive into it!
Definition
The recipe that you followed for baking a cake? That’s nothing but an algorithm!
Technically speaking, an algorithm is defined as a set of rules or a step-by-step procedure that are to be executed in a specific order to get the desired output.
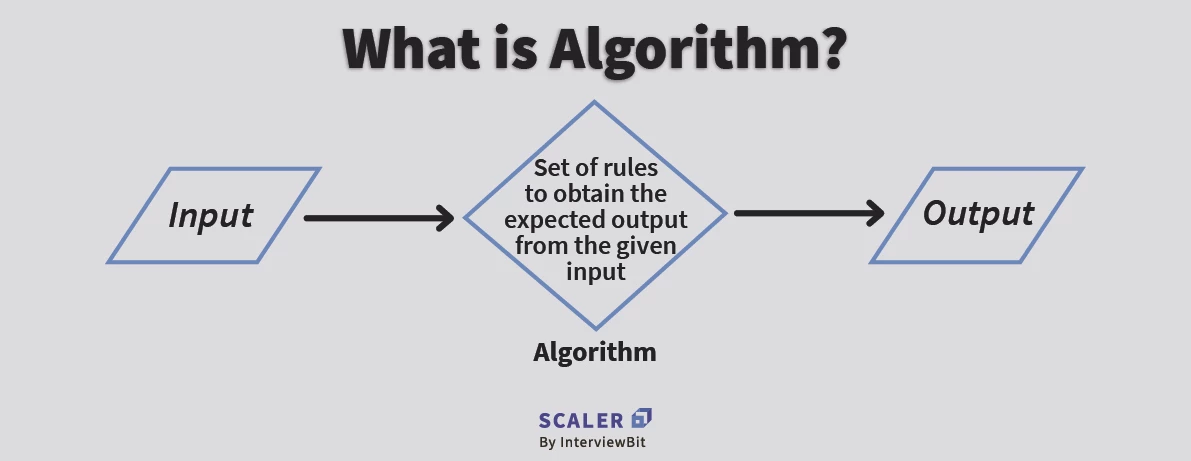
The formal definition of an algorithm is a finite set of steps carried out in a specific time for specific problem-solving operations, especially by a Computer. So basically, it is not the complete code, rather it is the logic that can be implemented to solve a particular problem.
Algorithms are independent of programming languages and are usually represented by using flowcharts or pseudocode.
Note: Pseudocode is nothing but the description of the logic or the code in plain, simple language.
So the next time you sit down to solve a math problem or even decide to go shopping with a specified shopping list in hand, remember that algorithms are around us all the time!
Characteristics of an Algorithm
A fact to be noted is that not all sets of instructions or procedures are an algorithm. A set of instructions should have all the relevant characteristics to qualify as an algorithm.
The characteristics of algorithm are as follows-
- Unambiguous– An algorithm should be clear and simple in nature and lead to a meaningful outcome i.e. they should be unambiguous. The recipe for baking a cake is the perfect example for this. It tells you the step by step procedure clearly, which leads you to bake a cake successfully. The situation could easily turn ambiguous if the recipe only has steps like “Add sugar.” This phrase is ambiguous or open to multiple interpretations- “How much sugar to add?” or “Add sugar to what?” are the kind of questions that can cause confusion
- Input– It should have some input values. In our scenario of baking a cake, our ingredients were the inputs
- Output– What did the ingredients of our recipe finally give us? A cake! The cake was our final output. So every algorithm should have well-defined outputs
- Finiteness– The steps of an algorithm should be countable and it should terminate after the specified number of steps. The recipe for the cake exhibits the characteristic of finiteness as you only need to follow the designated number of steps to get the desirable result
- Effectiveness– Each step of the algorithm should be effective and efficient enough to produce results. The effectiveness of an algorithm can be evaluated with the help of two important parameters-
- Time Complexity-It is nothing but the amount of time taken by the computer to run the algorithm. We can also call it the computational complexity of an algorithm. It can either be best-case, average-case or worst-case. We always aim for the best-case for effectiveness
- Space Complexity-It refers to the amount of computational memory needed to solve an instance of the problem statement. In simple words, it is the total space taken by the algorithm with respect to the input size. The lower the space complexity of an algorithm, the faster the algorithm will work
- Language Independent– Just like it doesn’t matter whether you bake a cake in a pressure cooker or an oven, you will eventually receive a cake as the end product. Similarly, algorithms should be language independent. In other words, the algorithm should work for all programming languages and give the same output
Data Flow of an Algorithm
Let us refer to our cake baking scenario once again-
The closed bakeries due to Covid restrictions was our problem. Our recipe was the algorithm. The ingredients were our input. The oven was the processing unit and finally, our cake was the output!
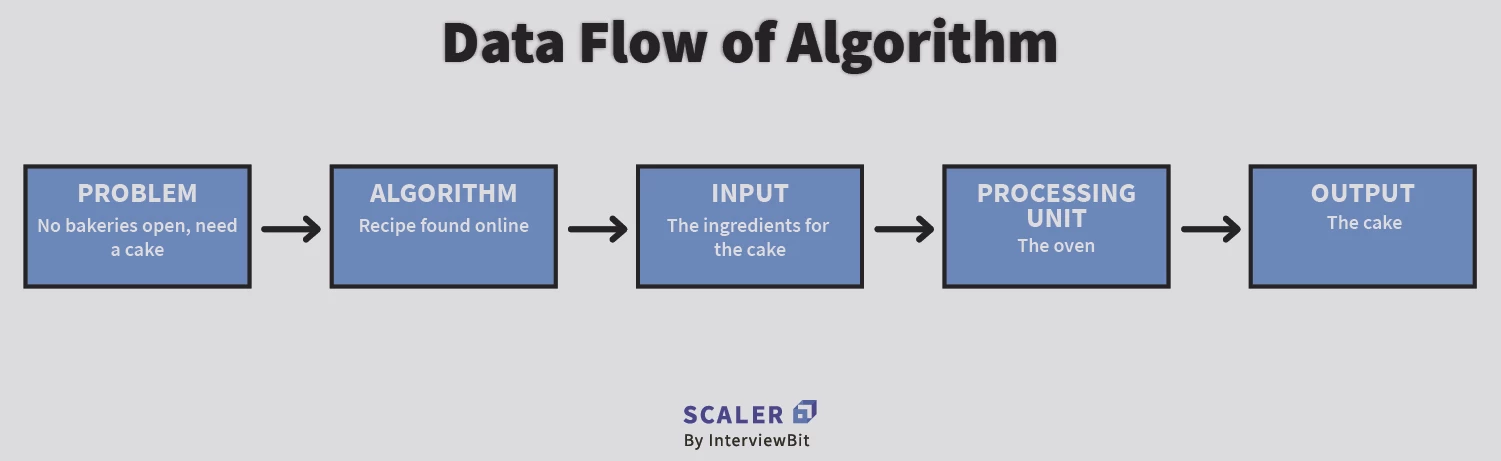
Well, with this scenario, we just saw how the dataflow of an algorithm works. Now we are going to break them down and take a closer look-
- Problem- The problem can be any real world or a programmable problem. The problem statement usually gives the programmer an idea of the issue at hand, the available resources and the motivation to come with a plan to solve it
- Algorithm- After analysing the problem, the programmer designs the step by step procedure to solve the problem efficiently. This procedure is the algorithm
- Input- The algorithm is designed and the relevant inputs are supplied
- Processing Unit- The processing unit receives these inputs and processes them as per the designed algorithm
- Output- Finally, after the processing is complete, we receive the favourable output of our problem statement
Why do we Need Algorithms?
Primarily, we need algorithms for the following two reasons-
- Scalability– When we have big real-world problems, we cannot tackle them on the macro level. We need to break them down into smaller steps so that the problem can be analyzed easily. Thus, algorithms facilitate scalability
- Performance– It is never easy to break down big problems into smaller modules. But algorithms help us achieve this. They help us make the problem feasible and provide efficient performance driven solutions
How to Write an Algorithm?

A simple Google search would tell you that there is no one “right way” to bake a cake. There are countless recipes available online- devised and tested by bakers around the world. Likewise, there are no predefined standards on how to write an algorithm.
The way we write algorithms is heavily influenced by the problem statement and the resources available. The common construct that is widely followed in case of algorithms is the use of pseudocode.
One thing that is appreciated while writing/ designing an algorithm is that the problem domain should be well-defined.
Factors of an Algorithm
While designing an algorithm, we must consider the following factors-
- Modularity- If a big problem can be easily broken down into smaller ones, it facilitates modularity
- Correctness- The analysis of the problem statement and consequently the algorithm should be correct. The algorithm should also work correctly for all possible test cases of the problem at hand. A test case is nothing but a specification of inputs, executing conditions, testing procedure and expected results, which can be developed from the problem statement itself
- Maintainability- The algorithm should be designed in such a way that it should be easy to maintain and if we wish to refine it at some point, we should be able to do so without making major changes
- Functionality- The steps of an algorithm should successfully solve a real world problem
- User-friendly- It should be easily understood by programmers
- Simplicity- It should be the simplest possible solution to a problem. By simplicity, we refer to the fact that the algorithm should have the best-case time complexity. The approach of the algorithm should be simple yet it should produce the desired results in a time-efficient manner, keeping both- time and space complexities- in mind
- Extensible- It should be extensible i.e. the algorithm should facilitate reusability. In other words, other programmes should be able to reuse it or extend for their own problem statement too
Example
Let’s start with a simple example of an algorithm-
Example 1: Design an algorithm to accept three numbers and print their sum.
Step 1-START
Step 2- Declare variables x,y,z and sum
Step 3- Read the value of x,y and z
Step 4- Add x,y and z
Step 5-Store the output of Step 4 in sum
Step 6-Print sum
Step 7- STOP
Example 2: Design an algorithm to find the factorial of a number and print it.
Step 1-START
Step 2- Declare variables fact, num and i
Step 3- Initialize variables as: fact->1 and i->1
Step 4- Read the value of num
Step 5-Repeat the steps until num=i
- 5.1- fact->fact*i
- 5.2- i->i+1
Step 6- Print fact
Step 7- STOP
Importance of Algorithms
The importance of algorithms can be classified as-
- Theoretical Importance- The best way to deal with any real-world problem is to break them down into smaller modules.The theoretical knowledge from pre-existing algorithms often help us to do so
- Practical Importance- Just designing an algorithm theoretically or using some aspects of pre-existing ones is not enough. The real-world problems can only be considered to be solved if we manage to get practical results from it
Hence, an algorithm can be said to have both theoretical and practical importance.
Issues While Working on Algorithms
The most common issue that we face while working on algorithms is- “How do I design it?”
Not all problems will have an easy solution and along with that, we need the solutions to be efficient as well. Sometimes, this may cause the programmers to feel stuck.
Conclusion
By now, you have successfully gathered a clear idea about-
- What is an algorithm?
- Characteristics of an algorithm
- The how and why of an algorithm
- The importance and issues
- Some easy to understand examples
The next time you do a task now, you will try to relate it with an algorithm. So start exploring and keep an eye out for learning more!
