Space Complexity in Data Structure
Learn via video course

Overview
Whenever we write an algorithm or code and run it in our computational device then it requires some space in our device to be executed. The memory here are required for storing the variables, data, temporary results, constants and many more.
Calculation and analyzing of this space complexity is important because in real world applications developers are bounded/limited to acquire the memory in the devices. The calculation of the space complexity also helps the developer to know about the worst case of that algo so as to improve that algo to perform in the worst case also.
Scope
- This article will let you know about the importance of space complexity.
- You will learn that how to calculate the space complexity of the particular algorithm from examples with the proper explanation.
Introduction to Space Complexity
Whenever we say that our algorithm is sufficient then it means that the algorithm is solving the problem in less amount of time while taking the least amount of space.
Let's take an example of sorting alogrithms like insertion and heap sort doesn't creates a new array during sorting as they are in-place sorting techniques but merge sort creates an array during sorting of elements which takes an extra space so if there is a concern of space then obviously one will prefer the insertion or heap sort.
Suppose you are provided with a task to sort the given array, so there are many sorting algorithms but you will choose the optimsed and efficient one always and for choosing that you have to analyze different algorithms on the basis of their space and time complexity.
So as we know that analyzing the algorithm is a much-needed task after designing an algorithm so as to increase the efficiency of an algorithm.
During analyzing any problem or algorithm you all may have encountered time complexity and space complexity.
Sometimes we ignore to calculate the space complexity but the fact is that space complexity is also an important parameter as the time complexity to analyze the efficiency of an algorithm or a problem.
Definition of Space Complexity
Space complexity is nothing but the amount of memory space that an algorithm or a problem takes during the execution of that particular problem/algo.
The space complexity is not only calculated by the space used by the variables in the problem/algo it also includes and considers the space for input values with it.
There is a sort of confusion among people between the space complexity and the auxiliary space. So let’s be clear about that, so auxiliary space is nothing but the space required by an algorithm/problem during the execution of that algorithm/problem and it is not equal to the space complexity because space complexity includes space for input values along with it also.
So we can say that space complexity is the combination or sum up of the auxiliary space and the space used by input values.
Space Complexity = Auxiliary Space + Space used for input values
Let's take an example:
#Sum Of N Natural Number
int sum(int n)
{
int i,sum=0;
for(i=n;i>=1;i--)
sum=sum+i
return sum;
}
So in the above example input value is 'n' that is constant which will take the space of O(1). Now what about auxiliary space, so it is also O(1) becuase 'i' and 'sum' are also constants.
Hence total space complexity is O(1).
Need To Calculate Space Complexity
As discussed above space complexity is an important parameter that must be calculated to analyze any algo/problem and check its efficiency.
Nowadays all systems come up with a large memory so this space is not considered for them but to make our algorithm more efficient so that it can run in less amount of space we have to analyze the space complexity.
Developers of real-world applications are constrained by the memory space of the systems they chose to run on. This is where space complexity comes into play, as we never want to run a function or process that consumes more space than the system has available at any given time.
How To Evaluate Space Complexity Algorithm
Now let’s understand that how to calculate the space complexity of an algorithm/problem.
We need to know the amount of memory used by different types of datatype variables,program instructions, constant values and few other things like function call, recursion stack(in recursion case) in order to calculate the space complexity. The amount of memory used by different types of datatype variables varies by os, but the way of calculating the space complexity continues to remain the same.
Language C compiler takes the following space:
| Type | Size |
|---|---|
| bool, char, unsigned char, signed char, __int8 | 1 byte |
| __int16, short, unsigned short, wchar_t, __wchar_t | 2 bytes |
| float, _int32, int, unsigned int, long, unsigned long | 4 bytes |
| double, __int64, long double, long long | 8 bytes |
Now let’s understand with an example that how to calculate the space complexity of an algorithm.
Example 1: Addition of Numbers
{
int a = x + y + z;
return (a);
}
So in the above example, there are 4 integer variables those are a, x, y, z so they will take 4 bytes(as given in the table above) space for each variable, and extra 4-byte space will also be added to the total space complexity for the return value that is a.
Hence, the total space complexity = 4*4 + 4 = 20 bytes
But for this example, this is the fixed complexity and because of the same variables inputs, such space complexities are considered as constant space complexities or so-called O(1) space complexity.
Example 2: Sum of all elements in an array
function sum_of_numbers(arr[],N){
sum=0
for(i = 0 to N){
sum=sum+arr[i]
}
print(sum)
}
So here this time there is an algorithm to find the sum of all elements in the array. For that we are passing the array(arr[ ]) and the size of array(N) to the created function. So here,
- In array(arr) the size of array is "N" and each element will take "4bytes" so the space taken by "arr" will be "N * 4 bytes"
- "sum" variable stores the sum of all elements and it will take "4 bytes" of space.
- "i" variable is used to iterate over all the elements in the array and it will also take "4 bytes" of space.
- Now function call, initialisation of for loop and print function these all comes under the auxiliary space and lets assume these all will take combinely "4 bytes" of space.
Hence, Total space complexity= (4*N + 12)bytes But these 12 bytes are constant so we will not consider it and after removing all the constants(4 from 4*N) we can finally say that this algo have a complexity of "O(N)".
Where the N varies according the size of the input array.
Example 3: Factorial of a Number(Iterative)
factorial(N){
int fact=1;
for (int i=1; i<=N; i++)
{
fact*=i;
}
return fact;
}
So here this time there is an algorithm to find the factorial of the number using iterative method. Now,
- "fact" is an integer variable which will store the factorial of the number(N), as a variable fact will take the "4 bytes" of space.
- "N" is an integer variable which stores the value for which we have to find the factoial, so no matter what value will, it will just take "4 bytes" of space.
- "i" is an iterator variable which stores the current value of iteration, so it will also take "4 bytes" of space.
- Now function call, initialising for loop and return function these all comes under the auxiliary space and lets assume these all will take combinely “4 bytes” of space.
Hence, Total Space Complexity = 4*4=16 bytes
As there is no variable which just constant value(16) is there so it means that this algorithm will take constant space that is "O(1)".
Example 4: Factorial of a number(Recursive)
factorial(N){
if(N<=1)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return (N*factorial(N-1));
}
}
So here this time there is an algorithm to find the factorial of the number using recursive method. Now,
- "N" is an integer variable which stores the value for which we have to find the factoial, so no matter what value will, it will just take "4 bytes" of space.
- Now function call, "if" condition, "else" condition, and return function these all comes under the auxiliary space and lets assume these all will take combinely “4 bytes” of space but the matter of fact here is that here we are calling that function recursively "N" times so here the complexity of auxiliary space will be "4*N bytes" where N is the number of which factorial have to be found.
Hence, Total Space Complexity = (4 + 4*N) bytes But these 4 bytes are constant so we will not consider it and after removing all the constants(4 from 4*N) we can finally say that this algo have a complexity of "O(N)".
Memory Usage While Evaluation
Whenever we execute any program in our computer then it takes some extra space from our computer. That extra space is taken by those programs is because of 3 main reasons which are stated below:
1. Instruction Space: Whenever we compile our code in the compiler then we need some memory in our computer or system to keep or store that code so as to execute it further. So instruction space is that space where that code is stored.
2. Environmental Stack: This space is used so as to store the address of the partially executed functions ( partially executed function is that function which calls the other function without executing itself completely ) because as we know sometimes the function calls itself(recursive) or any other function so the data of the previous function is stored/pushed onto the stack until further execution is needed, then the inner function is called.
Lets’s suppose we have a function X(), and Y() is the inner function of the X() so whenever the function X() will call the Y() inside it then the current data/variables of X() are stored/pushed onto the stack memory till the complete execution of Y().
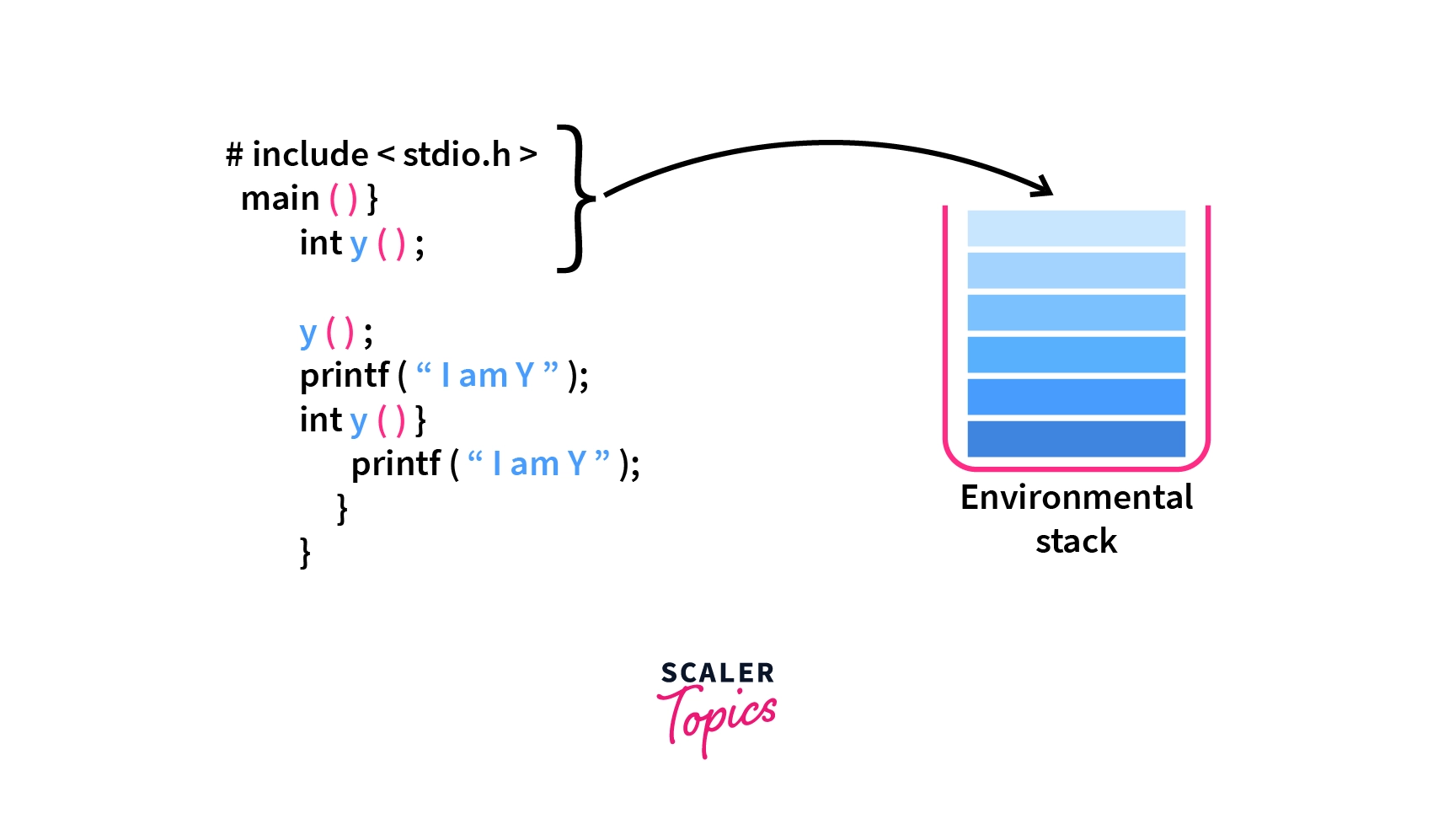
As in the above picture you can observe that at the time when "y()" function is called inside "x()" so all the current execution data which is executed till now(first 3 lines) gets stored inside the environmental stack and once the "y()" is executed then that partially executed data of "x()" will be retrieved back from the environmental stack.
3. Data Space: This space is used to store the data, variables, and constants of the program, and then they are updated during further execution.
But nowadays during the calculation of space complexity of any program, we just consider the data space and ignores the environmental stack and instruction space.
Examples of Space Complexity
Exampme 1
int sum(int a[ ], int n) # n is the size of array a
{
int x=0; # x takes 4 bits as integer variable
for (int i=0; i<n; i++) # i takes 4 bits as integer variable
{
x=x+a[i];
}
return x;
}
As the array a is of an integer data type with the size n, so the array will take 4*n bits of space in the computational device.
And n, x, and i will also individually requires 4 bytes each as of integer type, so the 3 combined will require 12 bytes of space.
So, Total space complexity = (4*n + 12) bytes, which increases linearly as the value of n increases and that’s why this is also known as linear space complexity or O(n) space complexity.
Exampme 2
int main()
{
int a=3, b=2, c;
c= a+b;
print(“%d”,c);
}
In the above problem, there are 3 variables a, b, and c of integer type, so each of them will require the 4 bytes of space.
So, the total space required = 4*3 =12 bytes.
Since there is no variable in the final space complexity and this program will always require the same amount of space that is constant (12).
Hence the space complexity required by this program will be O(1) or constant.
Space Complexity Table for Some Common Algorithms
| Algorithm | Space Complexity in worst case |
|---|---|
| Bubble Sort | O(1) "As it is in place sorting algorithm and requires the constant space for variables like flag, temp etc. " |
| Insertion Sort | O(1) " As it is in place sorting algorithm and requires the constant space for variables like flag, temp etc. " |
| Selection Sort | O(1) " As it uses constant space for 2 variables to swap elements and 1 for keep pointing on smallest element in unsorted array. " |
| Heap Sort | O(1) "As in this no extra array is needed because data is rearranged in original array so as to make it sorted." |
| Quick Sort | O(n) " As each recursive call will create a stack frame which takes up space, and the number of stack frame is dependent on input size n." |
| Merge Sort | O(n) "As in each recursive call 2 arrays are created " |
| Radix Sort | O(n+k) " As multiple arrays are created in this one based on size k and second one based on size n abd third one B is the output array. " |
| Fibonacci Series(Recursion) | O(1) " As the space here is directly dependent on the depth of the recursion tree which depends on the number of times the recursive function calls stack." |
| Shell Sort | O(1) " As it also does the inplace sorting of the elements by using the gaping sequence." |
| Bucket Sort | O(n+k) " Here n is the size of array and k is the number of buckets created. " |
| Counting Sort | O(k) " Here an auxiliary array is created of size k where k is the largest element in the given array." |
Conclusion
The conclusion is that whenever you write a program/algorithm then always try to make the space as little as possible so as to keep the space complexity of the program minimum.
After completing your program always analyze the worst-case scenario so that it can handle the large inputs and can have high adaptability and supportability.
The finalizing of the algo after considering the worst case will keep the resources(made using that algo) in proper condition without any heating issues.
Some Applications Of Analysing Space Complexity are:-
- Creators of real-world programmes are constrained by the physical memory of the platforms they plan to run on. That's where space complexity comes into play, as its obvious that we never ever want to run a function or process that consumes more space than the system has available at any one time.
- Helps to find to out the most optimized algorithm among all the algorithms, for particular type of problem.
- As nowadays flow of data is increasing rapdily so space complexity and time complexity combinely helps to design an efficient algorithm for performing any task.
