map() Function in Python
Learn via video course

Overview
The map() function in Python is a built-in function, where we can pass a function and any iterable (such as list, tuple, set, etc.), and it applies the given function to that iterable. After applying the function to all the elements, map returns a map object.
Syntax of map() Function in Python
Below given is the syntax for the map function in Python:
Parameters of map() Function in Python
In the image below, we have shown the parameters the map function in Python takes.
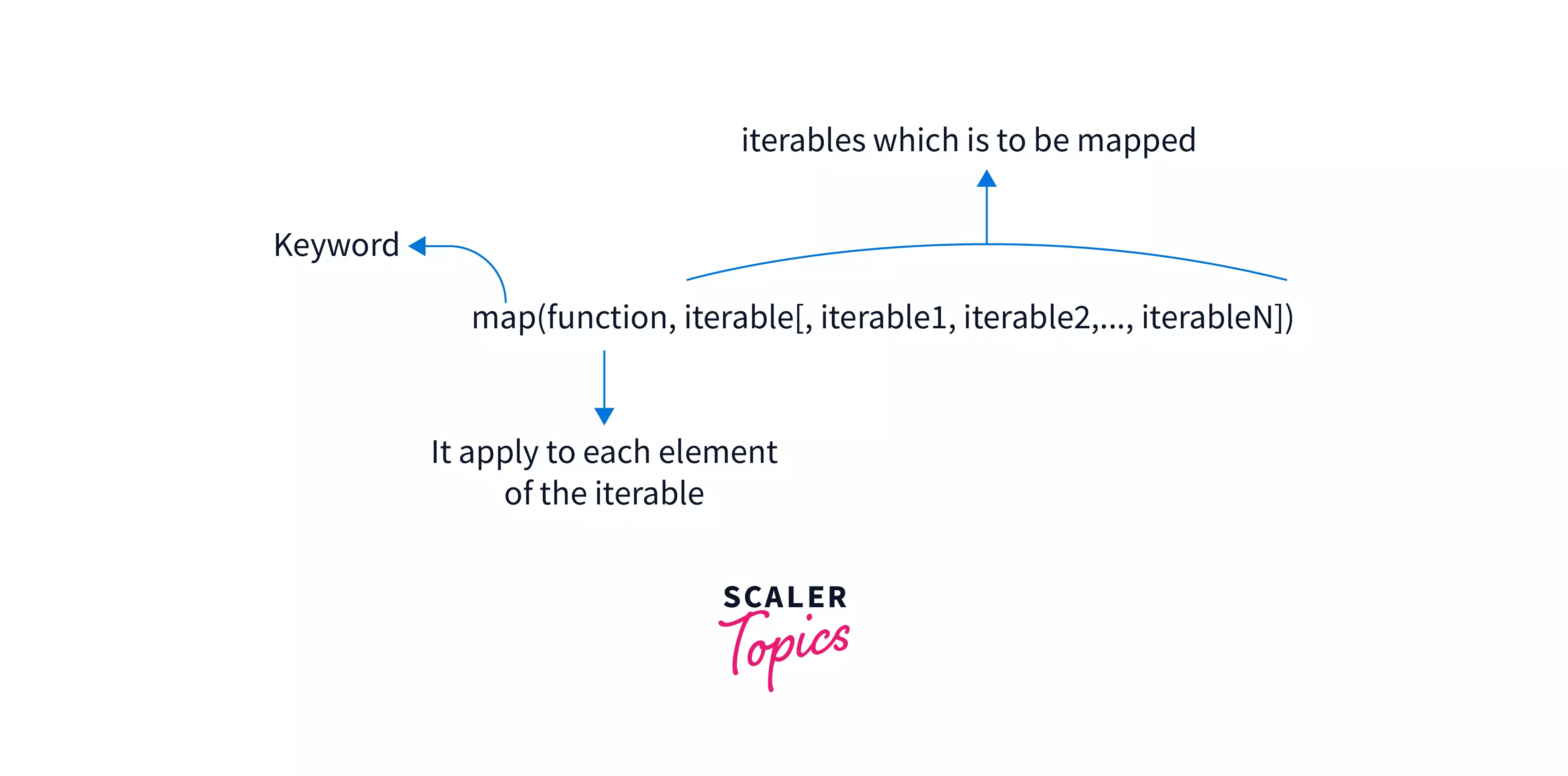
- The first argument to map() is a transformation function. The transformation function modifies each original item in the list, into a new (transformed) item.
- The transformation function can include built-in functions, classes, methods, lambda functions, and user-defined functions.
- The second, and later parameters are the collections of iterables over which we want our function to be applied.
- We can pass one or more iterables to our map() in python. The iterables can include list, tuple, set, etc. in python
Return Values of map() Function in Python
Map function in Python returns a map object after applying the given function to each item of the given iterable (list, tuple etc.).
We can then, pass over the map object to a list or tuple or set. Finally, we can fetch our result in the applied form.
Example of map() Function in Python
Code 1:
Output:
Explanation:
- Here we will calculate the square roots of the numbers using map(). Now, we define our user-defined function def square_root(n): to calculate the square root.
- Then we pass over that function, and our numbers list to our map() function. map() applies sqrt() to every value in numbers.
- We store our answer in result and print it. As output, we get our map object.
But, do we really want our result in this format? It is not even readable and understandable. So, to get our result into a readable format, we convert our map object into a list or tuple or a set, etc.
Output:
So, we convert our result into a list and finally, we get our converted result as the list. So, we should convert the result our map function returns(map object), into any iterable(like list, tuple, etc.)
What is the map() Function in Python?
So, till now we must have got a clear picture of map function in Python.

map() function in Python loops over each of the items of an input iterable (or iterables), and applies a transformation function(a function that can transform a particular value) to all the items of the iterable. Finally, map returns a map object.
Advantage of using map()
- map() is written in C programming language and is highly optimized, therefore, the loop map used internally is more efficient than the regular for loop we use.
- map has a better memory consumption compared to the normal loops because, with a for loop, we need to store the whole list in our system’s memory. But with map, we get only on demand, one item at a given time in our system's memory.
How to Use map() in Python?
To use the map function in Python, we should pass a transformation function and an iterable(or iterables) to our map function. The transformation function is applied to each of the items in the iterable and map object is returned.
Examples of map() in Python
Python map() with string
Code 1:
Output:
Explanation:
In the above example, we have used map passing to it a string. We transform the string into lowercase using our user-defined function to_lowercase .
Python map() with list
Code 2:
Output:
Explanation:
In the above example, we are converting a list of decimal numbers into binary. We are using our map function, and passing our transformation function along with the list.
Python map() with tuple
Code:
Output:
Explanation:
In the above example, we are converting a tuple of binary numbers into decimals. We are using our map function, and passing our transformation function along with the tuple.
Python map() with lambda
Code:
Output:
Explanation:
In the above example, we are using the lambda function as our transformation function. We are passing a list and our lambda function lambda x : x*x squares each of the numbers in the list.
Python map() multiple arguments
Code:
Output:
Explanation:
In the above example, we pass 2 iterables(lists) to our map function. And, we use a lambda function to compute the product of elements from each of the iterable(list). Hence, for obvious reasons, we can use multiple iterables with map().
What if the iterables are of different sizes? In that case, the map function is applied to the elements until one of them is finished.
Code:
Output:
Converting map to list, tuple, set
Code:
Output:
Explanation:
In the above example, we have converted the map object we received after transforming our list, into the list, set, and tuple respectively.
Conclusion
- map function in python applies a given function(transformer) to each item of an iterable (list, tuple, etc.) and returns an iterator.
- map function in Python uses a technique commonly known as mapping, to perform the above task.
- We also saw the syntax of map() and how can we use it with different kinds of functions like lambda function, normal function, and with different iterators like list, tuple, set, etc.
