How to Read a File in Python
Video Tutorial
Overview
File handling is available in Python and many other programming languages, allowing users to read, write, and perform other file-related actions. The file handling concept has extended to various languages, but the code is usually complex or lengthy. Like many others in Python, this notion is simple and quick to grasp. Python handles files differently depending on whether they're text or binary, which is essential. A text file comprises a sequence of characters in each line of code. A specific character known as the EOL or End of Line character, which might be a comma or a newline character, ends each line of a file. It ends the current line and tells the interpreter that a new one is starting.
Scope
- In this article, we will learn about one of the most important file operations, i.e. READING A FILE.
- We will learn about different modes of reading a file in Python.
- We will also learn about different built-in methods in Python for reading the files.
Introduction
Before we read files using python, we should first define files. To store any data, we use a contiguous set of bytes called a file. A file could be as simple as a text or an executable file. These file bytes are always converted to binary ( 0 and 1) format for processing by the computer.
Here are some types of files that Python can handle
- Text files
- Binary files
Other files that python can handle include csv files, excel sheets etc. But in this article, we will focus on the text and binary files.
What is the difference between the two files? In the text file, each line is terminated using a newline character \n. In contrast, a binary file does not have any such terminator, and the data of the file can be stored after converting the binary file into binary language that the machine can understand.
We can now move on to reading files with the help of python.
File Access Modes
When you open a file, you want to perform an operation on it. So depending on the type of operations you’d like to perform, you select an access mode in which you can open the file.
Typically, there are six access modes:
-
Read-only (‘r’): Denoted by r, this is the default mode for opening a file. If the file you wish to access does not exist, it raises an I/O error. With this access mode, you can only read a particular file.
-
Write only (‘w’): This is the access mode that you use when you want to write in a file that you’d like to open. Note, that in this mode, if your file already exists, then whatever you wish to write into your file, will get written, but will delete all the initial contents of the file. When a file does not exist, a new file will be created.
-
Append (‘a’): The append access mode allows you to write to opened files. Then what’s the difference between the append and write mode? Well, in the append mode, the initial contents of the file are not deleted. Whatever you wish to write in the file will be written after the initial contents of the file.
-
Read and Write (‘r+’): This mode allows you to read and write to a file. The handle is initially positioned at the beginning of the file. If the file does not exist, a file not found error is raised.
-
Write and Read (‘w+’): You might be wondering the difference between read and write mode and this mode. Since this mode is an extension of the write mode, whatever you write into the file will be written after the truncation of existing contents.
-
Append and Read (‘a+’): As the name suggests, you can read and append to a file in this access mode. Any data you wish to add will be added after the existing data.
Reading a File in Python
Now that we know the modes in which we can access a file, let’s get down to reading from it. But wait, before reading it, we must first know how to open a file. And here is where we will be using our access modes.
Opening a File in Python
To open any existing or non-existing file, we use the built-in open() function. One thing to note here is that whether you’re opening an existing file or you want to open a non-existing file ( by creating it) depends on your access mode.
The access modes that help create a new file if it does not exist are – w, w+, a, a+
Let’s see how we can use the open function to open an existing or non-existing file.
The syntax of the function is:
The 'r' just before the parameters is to prevent the characters in the file name from being treated as special characters. For example, if we have "\tapes" in the file address, then "\t" could be treated as the tab character, and an error would be raised. The 'r' represents raw, meaning the string does not contain special characters.
The open function gives us a file object on which we can perform operations. The parameters of the open function are the file name and the access mode in which you wish to open the file. In place of the file name, if the file isn’t in the same directory as the program, we can add the complete file path.
Usage:
Now, if you open a file, you must also close it.
Another important thing to note here is that when dealing with text files, it is recommended that you also specify its encoding as follows:
Closing a File in Python
To close a file, we use the built-in function close(). This function closes the file and frees the memory space that was acquired by that file. You can use the close function if you no longer need the file or if it is required in another access mode.
Usage:
That’s it!
To guarantee that the file closes, even if some exceptions are raised during file handling, a better way is to use the try … finally block. Any code in the try block is executed first. If any error is raised, it immediately stops executing the try block code and moves to the final block.
Now let’s get back to business. How do we read from the file?
Naturally, if you need to read from a file in python, you would use the r mode.
To read data from a text file in python, you have 3 possible methods:
1. The read() method in python:
The read method returns a string that contains all the characters of the file mentioned. There are no mandatory parameters to this function, but if you want to read a certain number of characters from the file, you can specify them as a parameter.
Now say the file example.txt has the following contents:
Hello World
I've learnt how to use the readline() function
To read all characters:
To read the first 5 characters:
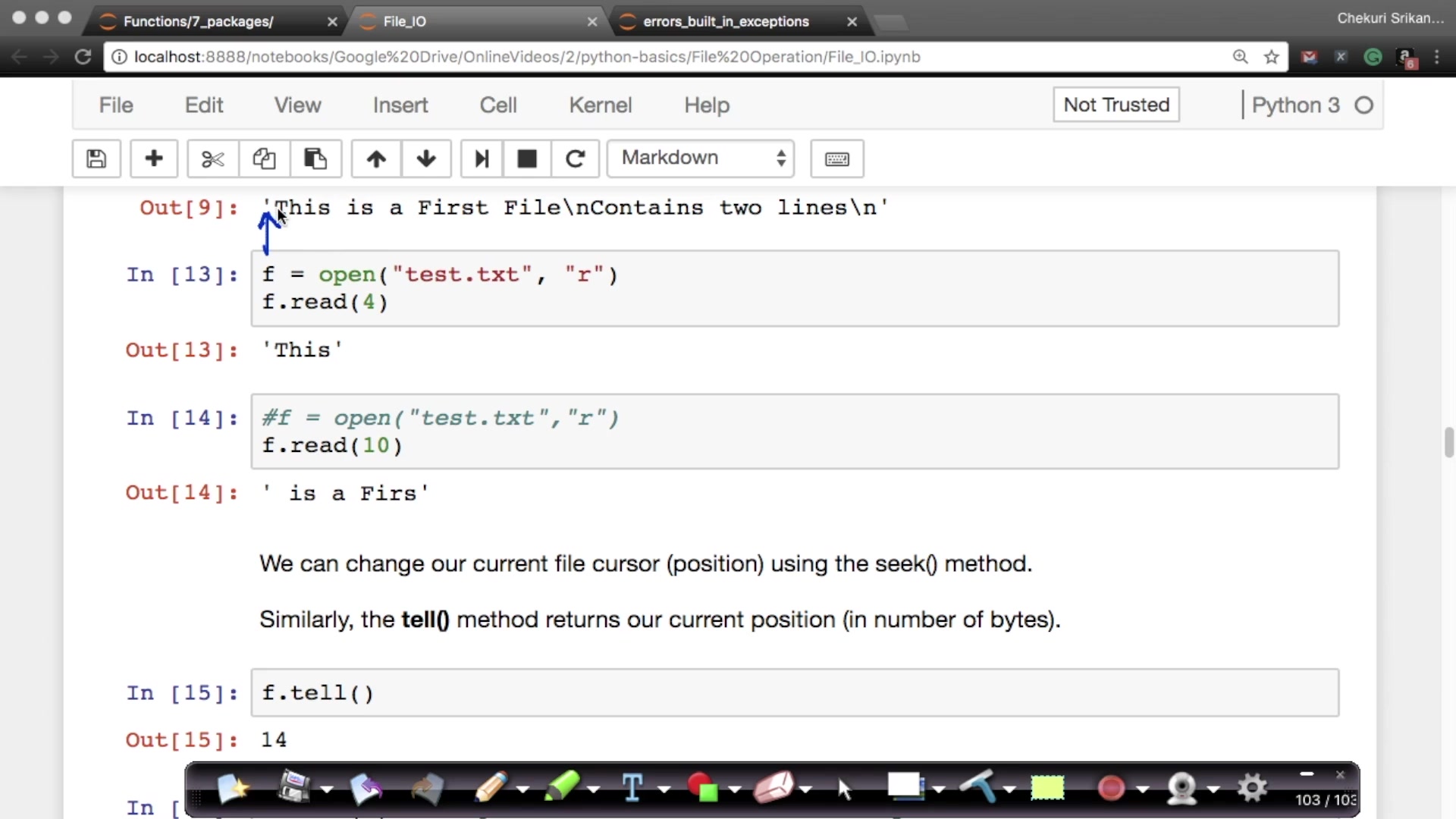
What if you wanted to read five characters but not from the current position? You want to skip the first 12 characters and print the following 5. How would you do that?
Python has a function that gives you the cursor’s current position while handling a file. And you can also ‘seek’ a certain position in the file.
The read() function only allows you to either read the file's entire contents or a certain number of specified characters. What if you wanted to read the first line or the third?
2. The readline() method in python:
The readline() function helps you read a single line from the file. You can run this function as often as you require to get the information. Every time you run the function, it returns a string of the characters that it reads from a single line from the file.
If you specify an n in the parameters, it reads n number of characters from that line in the file. If n exceeds the number of characters in the file, the method returns the line without reading the following line.
Usage:
Let’s assume the contents of the file are:
Hello World
I've learnt how to use the readline() function
Code to open:
3. The readlines() method in python:
As the name suggests, the readlines() method reads all the lines in the file and returns them properly separated in a list.
Usage:
Most of the time, you will not be using functions just like this. You might want to loop over the lines for some data you want to extract, etc. A more memory-efficient and fast way to do so is given below.
The contents of our new file are now:
This is a new file.
We have now learnt all read functions.
We are trying a new method
to loop over files.
The code to access the above contents of a file is:
Reading a Binary File in Python
In the beginning of this article, we discussed two file types. In all the above examples, we’ve seen how to read a text file in python. All the access modes, too, were only for text files. What about binary files?
To read/write to binary files, we have special access modes: ' rbandwb. Of course, rbis for reading andwb` for writing.
It is important to note here that the return type of any operations on binary files with these access modes will be in the form of byte strings and not text strings like in text files. Similarly, when you’re writing to files, the format must also be binary.
Example:
Reading Using the with open() Method in Python
Now in all the above examples, you must have noticed that we first open the file, and then close it after we’ve used it. There is another way of opening files that has a much cleaner syntax and provides better exception handling. The bonus here is that you don’t have to close the file after the operations you perform on it.
It is the with open() method.
Syntax:
Did you notice that we did not close the file here?
Here, you open the file as f, which means that f here is the file object on which you can do operations.
You now know all you need for read files using python! So, now you can start with reading files using python.
Conclusion
After learning about Reading Files in Python, here are some key points that will help you:
- In Python, we can handle files such as :
- Text files
- Binary files
- CSV files
- Excel Sheets etc.
- In Python, there are 6 access modes for file handling :
- Read only (‘r’)
- Write only (‘w’)
- Append (‘a’)
- Read and Write (‘r+’)
- Write and Read (‘w+’)
- Append and Read (‘a+’)
- We have 3 methods for reading text files in Python :
- read() method
- readline() method
- readlines() method