Scanner Class in Java
Learn via video course

Overview
A lot of time, while we are coding, it becomes necessary to take the input from the users. In Java we can do this using the Scanner class , using which we can take inputs of all in-built data types in Java like boolean, int , etc.
Introduction
Suppose you are writing a java program and you want to take input from the user. For example you want to take input of integer or float variable from the user. For the purpose Scanner class in java is used.
It is mainly used to read input of in-built data types like int, double, float, strings, etc. from the user, and this class belongs to the java.util package. Scanner class breaks the input into tokens/parts using a delimiter(a sequence of one or more characters that is used to separate independent values) which is by default whitespace. It is the easiest way to take input in Java.
The Scanner class inherits the Object class. Scanner class implements Closeable interface(which tells Java Virtual Machine that class can be cloned) and Iterator interface (cursor that is used to step through the collection of objects in java ). Declaration of Scanner class looks like:
Before using the Scanner class you have to import the Scanner class using the import statement as shown below:
How to Take Java Scanner Class Object
To create an object of the Scanner class in java, you need to pass System.in in the constructor of the Scanner class. System is a class in Java and in is a static variable of type InputStream . System.in represents the standard input stream. Here is the code snippet for the same:
Here the variable input represents the object of the Scanner class. While initializing the object input we are passing System.in object which is representing the standard input stream. You can use this Scanner object to call various functions provided by the Scanner class.
Note:
Here in the above example you are taking input from the user through the input stream, but if you want to read data or take input from the file then you can pass the object of class “File” to read the input from the file in the Scanner class constructor.
Suppose you want to take numerical input of a particular data_type. This data_type can be int, float, long, etc. For this purpose, the Scanner class provides the nextdata_type() function, where data_type is the data type of input.
You can call this function using the object of the Scanner class. For example, for taking input of an integer you can use nextInt() function, and for taking long as the input you can use nextLong().
If you want to take a string as input then the Scanner class provides the nextLine() method. All these functions are explained in the table below.
Working of Java Scanner Class
Scanner class in java reads the entire line of the input and divides that line into tokens using a delimiter(used as a separator i.e one or more than one character that separates the string into tokens or parts).
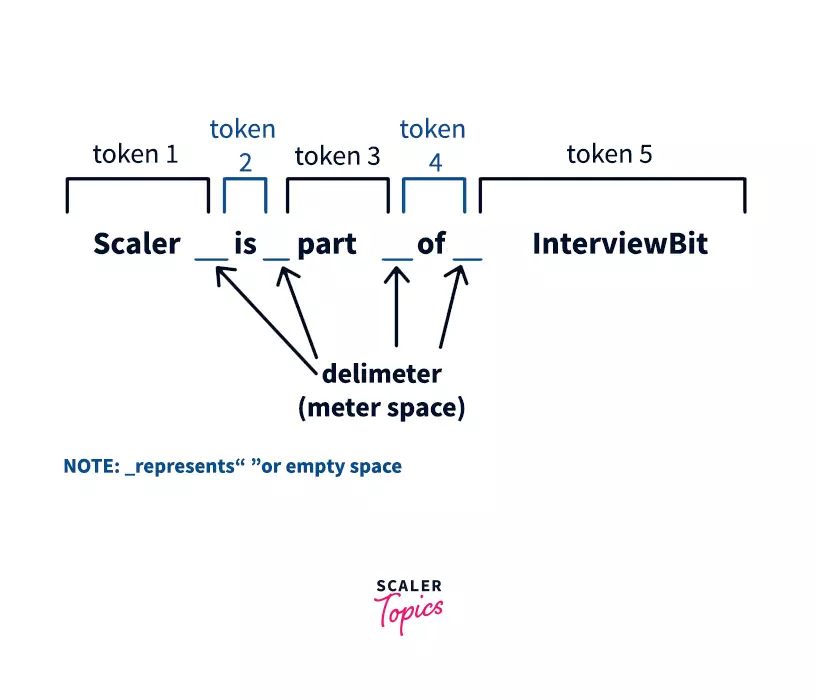
Tokens are small elements that can be understood by the compiler. For example: consider an input string,
“Scaler is part of Interviewbit”
In the above string, the scanner class object will read the entire line and divide the string into tokens using a delimiter. So the above string will be divided into the following 5 tokens: “Scaler”, “is”, ”part”, ”of”, and “Interviewbit”. Now Scanner object will iterate over each token and read each of token using its different methods that are discussed below.
Scanner class in java Methods
These are the few methods provided by the SScanner class in java to read input of various types with their description:
| FUNCTION | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| nextInt() | It is used to read an int value from the user |
| nextBoolean() | It is used to read a boolean value from the user |
| nextFloat() | It is used to read a float value from the user |
| nextDouble() | It is used to read a double value from the user |
| nextLine() | It is used to read a String value from the user |
| nextLong() | It is used to read a long value from the user |
| nextShort() | It is used to read a short value from the user |
| nextByte() | It is used to read a byte value from the user |
Incorrect para flow
Note:
If the user enters wrong input data for example in numerical input user enters text or string then the user will get an exception named InputMismatchException.
Apart from the above methods to take input, the Scanner class in java also provides many other functions:
| FUNCTION | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| hasNext() | It returns true if Scanner has another token for input or to mark whether the input is ended or not. If the user wants to know whether input has been ended or not then he can use this function. |
| hasNextInt() | It is used to check if the next token or input is of int data type or not. If that token is of int type, it will return true else false. |
| hasNextFloat() | It is used to check if the next token or input is of float data type or not. If that token is of float type, it will return true else false. |
| hasNextDouble() | It is used to check if the next token or input is of double data type or not. If that token is of double type, it will return true else false. |
| hasNextLine() | It is used to check if there is another line or string in the input or not. |
| hasNextLong() | It is used to check if the next token or input is of a long data type or not. If that token is of long type, it will return true else false. |
| hasNextShort() | It is used to check if the next token or input is of short data type or not. If that token is of long type, it will return true else false. |
| hasNextByte() | It is used to check if the next token or input is a byte or not. If that token is of byte type, it will return true else false. |
Scanner class in Java Example-1 : Taking different data-types input
Let’s take an example of Scalar employee, suppose Scaler wants to take the input of employee details from the user and you are creating the program for the same:
Input
Output
Note:
Here abc, 20, and 20000 are the input values.
Scanner class in Java Example-2 : Using hasNext function
Let’s take an example in which you have to find the sum of integers. Integer values have to be taken from the user and you have to print the sum of all integers.
Input
Output
Explanation
The Sum of integers given by the user in the input is 15 so 15 will be printed. The sum is calculated while integers are available in the input stream and that sum will be printed in end.
Conclusion
- In this article, we learned about taking input from the user in Java.
- We learned about Scanner class in Java. Scanner class is the simplest way to take input in java and it provides various methods (discussed above) to take input.
- You can use it when you have less time for writing the code fast due to its simple logic and usage.
