What is Big Data?
Learn via video courses
Before, Understanding what is Big Data, let’s understand what is data?
Data is a collection of information, which can be anything from a name, age to having a conversation in an interview. Everything is data. Some say data is the single most important thing of the 21st century. It’s like oil for this century. So, now we know what data is. So, let’s understand what “Big Data” really means.
So, by the name you might be thinking, the collection of large amounts of data is “Big Data”. It’s not exactly wrong but there is more to this definition. When a large volume of data, which can be both structured and unstructured. But, it’s not the amount of data that’s important, it’s how that data is studied for a better understanding of the situation.
Let’s take an example, In 2014 there was a massive forest fire around San Francisco. Around 6 were injured and 1 died. Around 60 million USD was spent on restoration. But after that incident there wasn’t a single forest fire around San Francisco. Why? Because during that fire tremendous amounts of data were collected which was later studied and suitable steps were then taken to avoid another similar incident in the future. Not only with the help of Big Data forest fires were avoided in the future but they saved the US millions of Dollars.
History of Big Data

The word Big Data was coined in 1987 by John Mashey, but its roots are quite old. Ideally, if we talk about data, it dates back to the age when humans were discovered by fire or even before that because ideally, the meaning of data is storing information. It doesn’t need to be stored in a SQL or no-SQL database. Our mind is quite capable of storing information. But let’s not deviate from our topic of discussion which is “Big Data”.
Early traces of Big Data dates back to the 17th Century when John Graunt was studying the tremendous amount of data related to a disease called Bubonic Plague. But, if we technically speak in terms of technology it was 1990 during the initial days of the internet when the study of large volumes of data was started by big organizations.
Why is Big Data Important?
Big data is useless if we don’t know what to do with that data. So, if we are aware of the source of data and how it was analyzed, we may use it as a solution to our big data model. Companies use big data to provide us with better services, targeted marketing campaigns, etc to increase their revenue and customers. Organizations that know the importance of Big Data have a competitive advantage over their competitors. Organizations like Google uses Big Data to provide us with ranked results in terms of relevance, Spotify uses it to develop personalized content like customized playlists, and similarly, many other companies like Facebook and other giants use it to provide personalized results and services.
Big Data is not just limited to Tech Companies or big corporations, but every field in some way or the other uses Big Data. Like in the health sector, doctors and researchers use big data to identify the disease and the risk factor, and a combination of previous records and present conditions helps researchers get more information regarding the illness.
How Big Data Works?
To know how big data works, let’s understand the definition once again. Big data is a large volume of data that is analyzed for better understanding. So, what is this understanding? Understanding is the result we get after the choice of decisions we made. So, the working of Big Data can be summarized in three words i.e Big Data, Analytics, and Decisions.
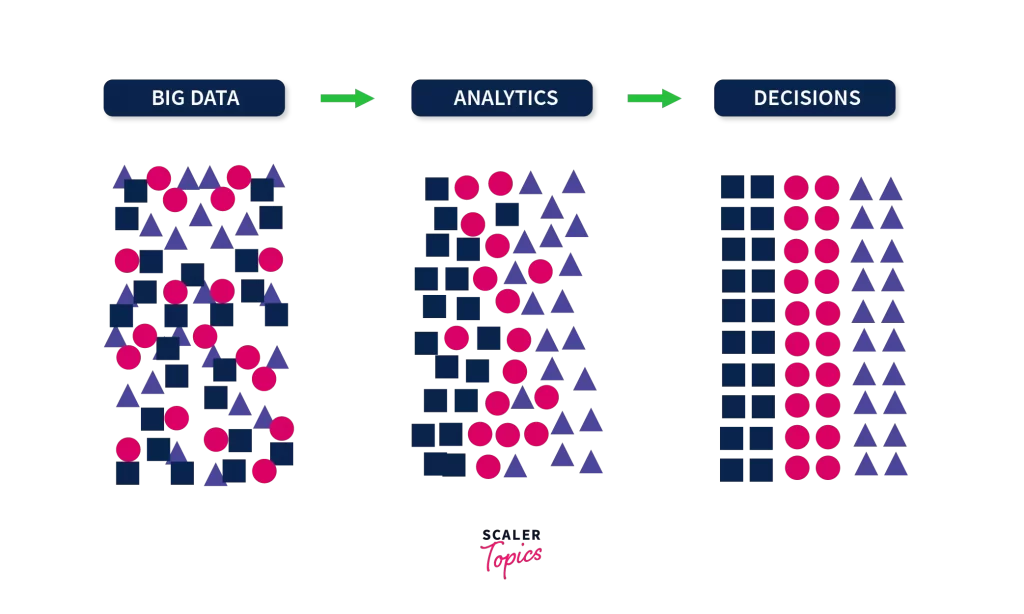
Since we know that our end goal is to analyze data and reach a decision. So, to do that there are 3 main actions so that we reach our end goal.
Integration
collected data from a variety of sources, such as Datasets. As a result, integrating that raw data will be demanding. What we do is the process the data and format it correctly. Which algorithms are available to us? What kind of data is available?
Management
Storing the data is the next step. It can be done either by storing in large server rooms or the cloud.
Analysis
After the data is formatted in our desired form and then stored somewhere safe. Yeah, that decision will help us put that data to work. We start to analyze it using required tools and reach a decision. Few most popular tool for Big-data analysis is Hadoop, Spark followed by many others. Yeah, that decision will help us put that data to work.
Types of Big Data
So much discussion on What is Big Data, but now it’s time to understand types of big data.
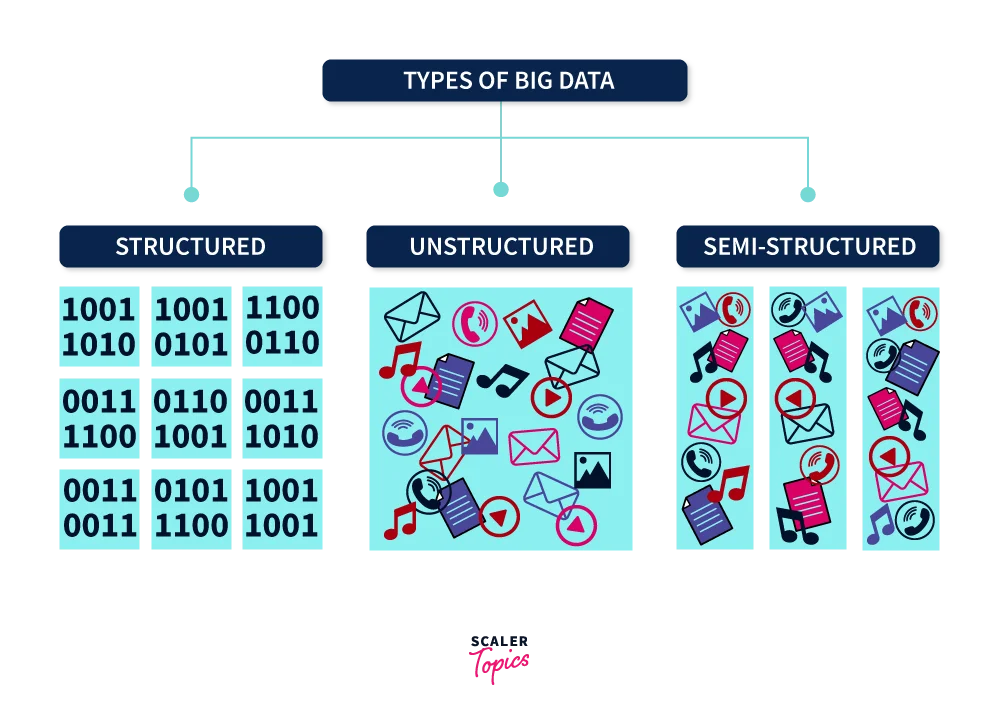
Structured Data
When the data is processed, stored, and retrieved in the desired format, and can be stored in relational databases, which makes it easier to analyze. Names, dates, addresses, credit card numbers, and other structured data are examples.
Unstructured Data
Unstructured data is information that lacks a specific format and is stored in original form without any presets. It’s demanding and time-consuming to process and analyze unstructured data. Rich media like Data from the media, entertainment industries, and surveillance data are examples of unstructured data.
Semi-Structured Data
When the data is not segregated properly but yet contains some vital information. Email, NoSQL databases, and other semi-structured data are examples.
Characteristics of Big Data
Some say there are 3V’s and some say 5V’s but as per my knowledge, there are 6 V’s. So, what are these 6V’s? We can model the entire Big Data into 6V’s for better understanding. Those are Veracity, Value, Variety, Volume, Velocity, and Variability. So, let’s discuss them one by one.

Volume
Volume is a huge set of data that may or may not be in our desired format and may need further processing to extract valuable information. An example of a high volume of data can be daily transactions through Online payment services like UPI, credit card, etc.
Velocity
Velocity is the rate of growth of data. Since big data is rapidly changing or keeps getting updated in data storage, we need to process structured and unstructured data and keep updating our data stores to take advantage of the information. Social media posts are an example of data generated at a high Velocity.
Variety
It refers to whether the data is structured semi-structured or unstructured. Which we talked about earlier. Variety of data can be anything from email, phone number, XML file, audios, videos, etc.
Veracity
It is the quality, validity, and trustworthiness of the data. Suppose you are willing to go to a restaurant, you search on google to find out which one will be best suited for you. But due to excess unstructured data from all the sources, you end up getting confused. Here comes the use of hashtags which helps you to sleek down your interest, and along with suggestions, you also get the images of that place that has been shared by other customers thereby, building a sense of trust in you that other people liked it too. This is how veracity can be justified through this example and helps us understand its importance in explaining big data.
Value
It is the most important V of big data, which can be defined as the ability to transform the data into business. So, to better grasp it, let’s look at an example. If data lacks Value, we will not be able to use it in other Vs to solve problems associated with a specific hypothesis and thus won’t transform it for successful business activities.
Variability
It refers to data whose meaning changes over time. Organizations frequently need to create complex systems to comprehend context and decode the exact meaning of raw data. Lets understand this change through a real life example. Let’s understand this change through a real-life example. Every hostel student might relate to it. Suppose every week Mess serves paneer. Although that paneer does not taste good but every week there is a change in taste. This change is variability, why does the taste change? Because on someday chef pours extra spices and on other days he does not. The same is true for data, which might have an impact on the quality of your data if it is constantly changing.
Big Data Use Cases
Big Data is used in different industries and domains. Let’s understand with a few example use cases.
Recommendation Engines
While watching the usual Netflix and prime. These streaming services tend to show us a few shows under “recommended for you”. So, this recommendation system works with the help of big data where large amounts of structured and unstructured data can be gathered just from a few clicks and this information helps companies predict the recommendations for the user.
Financial Fraud Detection
With the use of Big Data and machine learning algorithms, Even if there are any subtle changes in consumer’s purchase or credit card activity, it can be automatically analyzed and can be marked for fraud because of this each year these financial institutes millions of dollars in fraud. Even in the Insurance sector because of big data billions of dollars are saved each year as claims can be analyzed and a similar machine learning model then detects the potential fraud.
Health Care Sector
Doctors, Researchers, and health care companies are rapidly adopting big data solutions to solve different problems. Researchers and doctors can conduct more effective research for some of the noncurable diseases like HIV, Cancer, Alzheimers and can develop more effective drugs by analyzing the pattern. Even hospitals are adapting to big data solutions to do customized ways of testing as opposed to trivial ways of testing and in some countries, big data helps in faster and more efficient analysis of healthcare information.
Agriculture and Food Industries
Big data is used to improve the quality and quantity of crops by using geospatial data, graphical data, seismic activities, etc. Due to the growing population, improving the quantity of food has been the priority in the last thirty years. Due to big data, the fight against global hunger has been made possible.
There are many other use cases but to get a basic gist of how useful big data is in the 21st century this must be enough.
Big Data Challenges
Many organizations are still stuck at the initial stage of implementing big data into their organization. Let’s try to understand the issues of these challenges.
Incomplete Understanding of Big Data
Sometimes organizations are unable to understand what is data? Why is it so important? because of this integration of required algorithms to analyze the data becomes really difficult. The solution to this problem is to educate the employees regarding “big data”.
Exponential Data Growth
90 percent of the data created in the last 2-3 years. One of the biggest challenges is the exponential growth of data as time goes on. Since most of the data is unstructured and comes in the form of the document, videos, etc. Which is difficult to analyze. Since data is growing exponentially, it’s becoming difficult to store this data.
Security of Data
Companies spend so many resources for understanding, storing, and analyzing the data they often forget to prioritize the security part. So, they try to push the security part for the later stages because of which data breach is possible. A solution for these companies is hiring cybersecurity professionals to protect their data.
Data Integration
Since data can be in any form from structured data like phone numbers to unstructured data like videos. So, integrating these data is difficult, but at the same time, data integration is crucial for processes like analysis, reporting, and forecasting. So integration has to be error-free. Companies can solve these problems by purchasing the right technologies like IBM InfoSphere, Microsoft SQL, etc.
There may be other challenges faced while implementing big data but these key challenges are really important to overcome for better analysis of data.
Big Data Best Practises
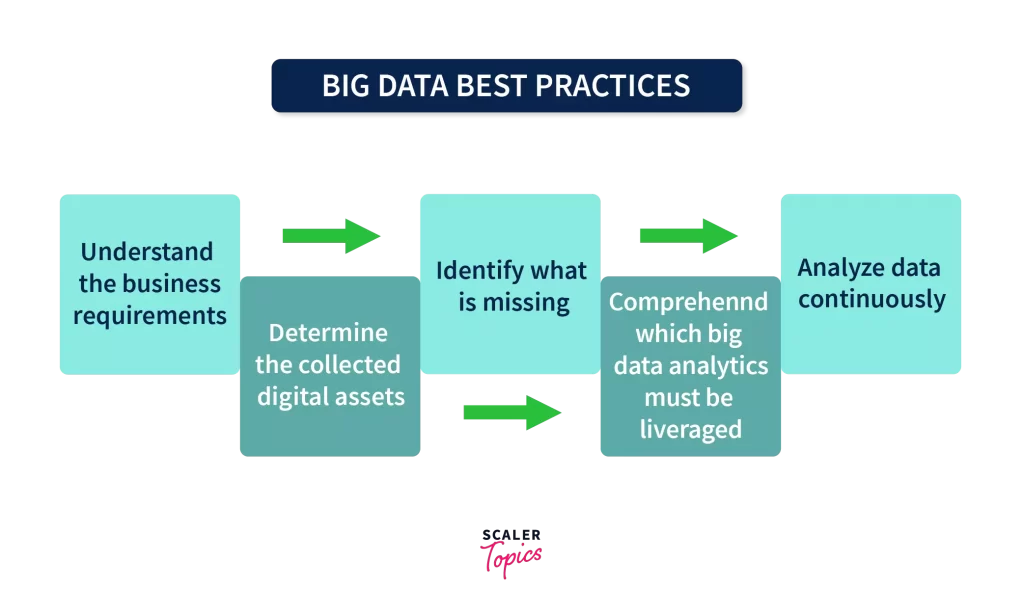
Since now we have a basic understanding of big data, let’s talk about the best practices of Big Data.
Establishing a Plan
Setting up a sense of direction for our goals and objectives.Since, According to that plan we tend to start working on the big data solution. This plan needs to start from the very foundation so that we can reach our objective. Consider this scenario: you’re a Big-data engineer, and your employer wants to develop a Netflix-style recommendation system. As a result, you won’t be able to meet all of the requirements at once. You must begin with the foundation and then establish a few benchmarks with deadlines, which you must meet to complete the project.
Learn About Your Data
Companies tend to have an ocean full of data but the problem is they need to understand their data and they’re objective to analyze that data. With that analysis, they can work on their goal. So, a Proper understanding of data will help organizations save time and resources.
Learn About the Missing Data
In the second point, we talked about the need to understand the data we have. But now let’s try to know about the data that we don’t have. In certain of the objectives, we may require more information that we may not have at the time. For that missing information, we may look into the data of past solutions. From the data gathered from the past, we can leverage its use in the future by creating different datasets.
Which Data Needs to Be Used
After collecting and analyzing the data, we need to use technologies and tools to understand our analysis. This analysis is done based on our objective whether we want to study fraud detection, predictive analytics, etc.
Continuously Lookout for Data
The organization must be aware of the data flowing. Analyze the health of the data occasionally so that we don’t miss some vital information. Companies must be informed of the practices happening to extract data and keep their data stores updated.
Advantages of Big Data
Cost Optimization
One of the biggest advantages of big data is significantly reducing the cost of storing, analyzing, and processing large amounts of data. For example- Usually, E-commerce companies are getting a return of 1.5 times of actual shipping cost. So, by using big data, organizations try to predict the profit from that particular product or service.
Improve Efficiency
Big data has the potential to significantly improve operational efficiency. By gaining feedback from customers, organisations analyze and interpret those feedbacks from those customers. Which further allows companies to create personalized products and services.
Innovation
Predictive analysis helps to design the best possible solution by analyzing the feedback and reviews from customers. Which gives an organization an edge over other competitors.
Diversify the Revenue
Big data can help increase the revenue of the organization by diversifying its assets in different sources by creating a new revenue system.
Disadvantages of Big Data
Privacy and Security concerns
One of the drawbacks is security concerns. In reaction to ongoing data breaches, governments have enacted more stringent rules, forcing firms to continue investing in infrastructure that conforms with these laws, which costs a fortune to these companies.
Difficult to Handle
Because of the volume and variety of data, as previously stated. Integration, handling, and operation become too complicated. As a result, companies must hire more specialized personnel, which increases their spending budget.
Data Is Rapidly Changing
The fact that technology is continuously changing is a possible disadvantage of big data. Organizations confront the very real risk of investing in a certain technology just to see something far superior emerge a few months later. This drawback of large data was ranked fourth among all the potential obstacles faced by Syncsort respondents.
When comparing the benefits and drawbacks of big data, most businesses decide that the benefits outweigh the drawbacks. However, before initiating a new big data project, the relative downsides and benefits of big data should always be carefully considered.
