While Loop in C++
Video Tutorial
Overview
Loops are an indispensable part of programming in C++. A loop is used to execute a piece of code multiple times. Loops in C++ consist of two types i.e. entry and exit controlled loops. While loop is a type of the entry controlled loop which initially checks the condition and if the condition is true, then execute the loop body. It is basically used when the count of iterations is not fixed. One or more than one while loops can be used inside another while loop in the nested form. If the condition of the while loop never fails then the while loop will run infinitely.
Scope
- The article gives a brief introduction to loops in C++ followed by the definition of the while loop in C++ along with the flow diagram and step-wise execution.
- The working of the while loop is explained with the help of various examples.
- A brief introduction of the do-while loop along with how it differs from the while loop is also illustrated properly.
Syntax for While Loop in C++
The C++ language provides the following syntax for the while loop:
Parts of the While Loop in C++
The while loop consists of three parts:
- Test Expression
- Loop Body
- Update Expression
Test Expression
The test expression acts as a gateway that tells the while loop whether to execute the loop body or not. It gives a boolean result that directs the while loop. The while loop keeps on executing till the test expression returns true. As soon as the test expression returns false, it stops the execution.
Loop Body
After the test expression returned true, a block of code or loop body gets executed. The major part of the loop is filled with the loop body.
Update Expression
The update expression is used to update the variable used in the test expression. It is a part of the loop body and hence its execution occurs along with the loop body. If this expression gets wrong or missed then the loop may run infinitely.
Flow Diagram with step-wise execution
Flow Diagram of While loop in C++
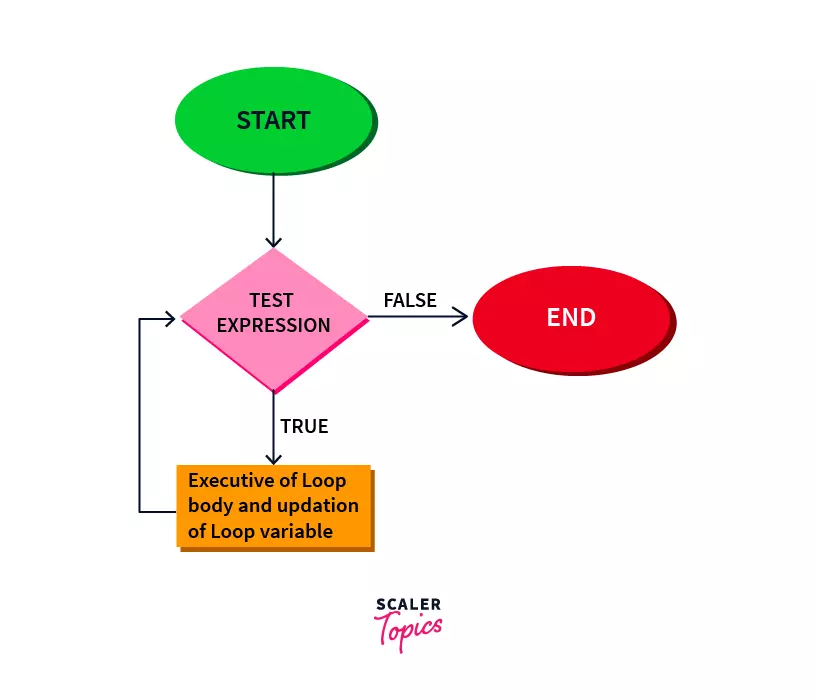
The flow diagram can be interpreted through the step-wise execution of the while loop is given below.
Step-wise execution of the C++ while loop
STEP 1: The program control enters the while loop.
STEP 2: The control initially reaches the test condition.
STEP 3: The test condition is checked.
The block of code inside the loop gets executed if the test condition returns true and the control immediately gets out of the loop if the test condition returns false.
STEP 4: The control then executes the block of code present inside the while loop.
STEP 5: The loop variable gets updated along or after the code execution.
STEP 6: The control moves to STEP 2 till the test expression returns true.
STEP 7: When the test condition returns false, the execution of the while loop ends.
Example for While Loop in C++
In computer programming, a loop is used to accomplish the job of executing a block of code recurrently. Loops in C++ consists of two types:
- Entry controlled loops
- Exit controlled loops
Entry controlled loops: It is a type of loop which initially checks the test condition and then executes the loop body. FOR and WHILE loops are the types of entry controlled loops.
Exit controlled loops: It is a type of loop which initially executes the loop body and then checks the test condition. DO-WHILE loops are the types of exit controlled loops.
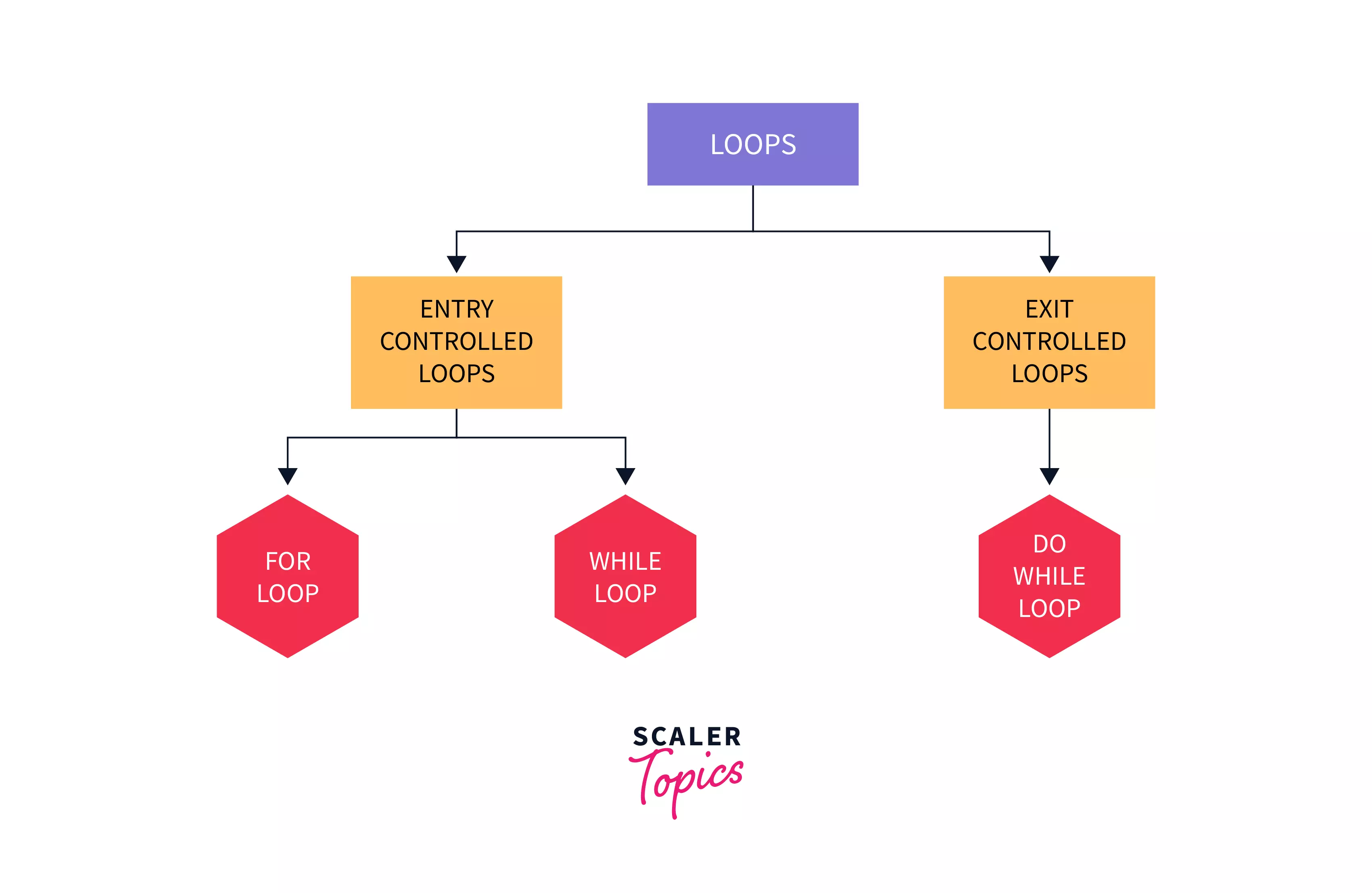
While loop is one of the entry controlled loops which initially checks the condition and if the condition returns true then execute the loop body and update the loop variable and gets out of the loop body if the condition returns false. Unlike the other entry controlled loop in C++ i.e. for loop where the number of the iterations is already known, in a while loop, the number of iterations may or may not be known. While loops are mainly used in the cases where the number of iterations is unknown.
Basic Example: Program to print "Scaler Topics" four times using while loop in C++
Output
More Examples for while loop in C++
Example 1: Program to reverse a number using while loop in C++
output
Step-wise explanation of above code:
Step 1: Initialization of the number to be reversed in 'n'.
Step 2: Initialization of the output variable i.e. reverseOfn to 0.
Step 3: Checking the test condition ie. n > 0
Step 4: Entering in the while loop.
Step 5: Multiplying reverseOfn by 10 and adding the remainder of n divide by 10 to reverseOfn.
Step 6: Update the loop variable n by n/10.
Step 7: Print reverseOfn.
First iteration: The value of reverseOfn becomes 4 and n becomes 123.
Second iteration: The value of reverseOfn becomes 43 and n becomes 12.
Third iteration: The value of reverseOfn becomes 432 and n becomes 1.
Fourth iteration: The value of reverseOfn becomes 4321 and n becomes 0.
Example 2: Program to print first n numbers of Fibonacci series using while loop in C++
output
Step-wise explanation of above code:
Step 1: Initializing a=0 and b=1.
Step 2: Check if n is smaller than 1, if yes, then print Invalid input and return.
Step 3: Print 'a' and initialize the loop variable s=1.
Step 4: Checking the test condition s<n.
Step 5: Entering in the while loop.
Step 6: Print 'b' and add a and b and put the result in c.
Step 7: Update 'a' by 'b' and 'b' by 'c'.
Step 8: Increment the loop variable s by 1.
Nested while loops in C++
Nested while loops are represented by while loops inside a while loop. There can be one or more than one while loops inside another while loop. The while loop that contains other while loops is often called the outer while loop or parent while loop. The while loops inside the outer while loop are often called inner or child while loop.
Example 3: Program to demonstrate nested while loop in C++
output
Infinite while loops in C++
Infinite while loops in C++ are the never-ending loops. The test expression in such while loops always results true. Missing or wrong update expressions may cause infinite while loops to occur.
Example 4: Program to demonstrate infinite while loop in C++
output
Explanation: The update expression loop variable decreases every time and it is always going to be less than 5. Hence the loop will run infinitely.
Example 5: Program to Display the elements of an array using while loop in C++
output
Difference between while and do-while loop
Do-while loop in C++
Do-while loops are the exit controlled loops that initially execute the loop body and then check the test expression. If the test expression returns true, then control continues executing the loop. If the test expression returns false, then the control gets out of the loop.
Syntax:
Tabular difference between while and do-while loops in C++
| While | Do-while |
|---|---|
| It checks the test expression before executing the loop body. | It initially executes the loop body and then checks the test condition. |
| It is an entry controlled loop. | It is an exit controlled loop. |
| If the test expression initially returns false, there is no execution of the loop body. | If the test expression initially returns false, still there will be a single execution of the loop body. |
| Absence of semicolon after the test expression. | Semicolon is mandatory to be placed after the test expression. |
| Syntax: while(test condition) { // loop body} | Syntax: do { // loop body } while(test condition); |
Conclusion
- A loop is used to accomplish the job of executing a block of code recurrently.
- Loops in C++ consist of two types i.e. entry and exit controlled loops.
- While loop is a type of the entry controlled loop which initially checks the condition and if the condition is true then execute the loop body.
- No other loops can work if the number of iterations is not known except while loop.
- Process of execution of while loop in C++: Checking test condition —> Execution of loop body —> Updation of the loop variable.
- A while loop containing one or more than one while loop is known as a nested while loop.
- A while loop in which the test expression never returns false is known as an infinite while loop.
- Do-while loops are the exit controlled loops that initially executes the loop body and then check the test expression.
